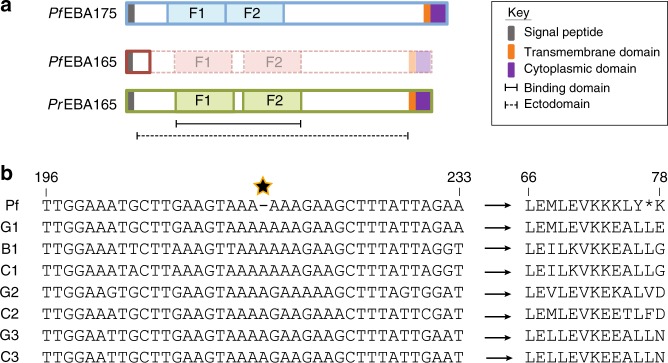
Fig. 1.
EBA165 frameshifts are specific to human-infective Laverania parasites. a Cartoon of EBL protein structure and domains. The erythrocyte binding domain of each protein is split into two Duffy Binding Like (DBL) erythrocyte binding domains (F1, F2). Bold outlines indicate translated amino acid sequence. In P. falciparum, the presence of a frameshift mutation eliminates translation of the majority of the protein, including both DBL domains, unlike the homologous protein in Plasmodium reichenowi (PrEBA165) or the major P. falciparum glycophorin binding protein, PfEBA175. The dashed/faded region of PfEBA165 depicts the protein structure that would be produced if frameshifts are corrected. b Alignment of Laverania EBA165 orthologues spanning the single base pair deletion (starred) universally conserved in 2517 globally distributed clinical P. falciparum isolates. Sequences displayed are from one isolate for each Laverania species (G1, P. praefalciparum; C1, P. reichenowi; B1, P. lomamiensis; G2, P. adleri; C2, P gaboni; G3, P. blacklocki; C3, P. billcollinsi). All seven non-human-infective Laverania species lacked the single nucleotide deletion (left hand side), eliminating the premature stop codon present in PfEBA165 and resulting in intact amino acid sequences (right hand side). Residue numbers are indicated above the alignments and are based on the PfEBA165 sequence. Partial alignments of ape Laverania PfEBA165, along with a frameshift corrected P. falciparum sequence, are shown in Supplementary Fig. 1