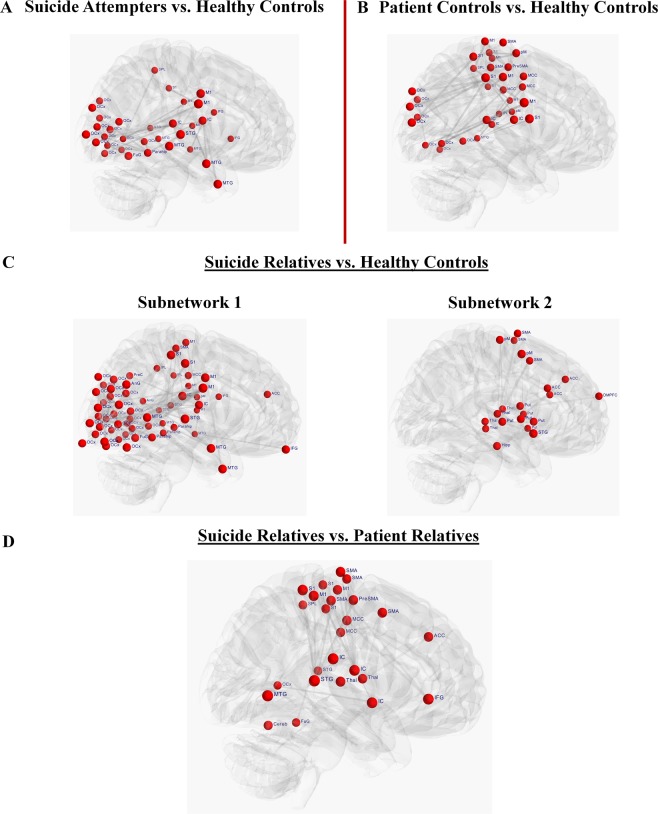
Figure 4.
Group comparisons in functional connectivity matrices using Network-Based statistics (NBS). Significant group differences between functional connectivity (FC) matrices using the framework of the network-based statistic (NBS) introduced by Zalesky et al.33 are illustrated. NBS is a validated nonparametric method to avoid the multiple comparison problems due to mass univariate significance testing in FC. (A) NBS analysis revealed a single network of decreased FC in suicide attempters as compared with healthy controls (p = 0.04, FWER) comprising a total of 33 nodes connected by 34 edges and including occipital regions (OCx), right fusiform gyrus (FuG), middle (MTG) and superior temporal gyrus (STG), left inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), right posterior insula (IC), bilateral primary motor (M1) and left somatosensory (S1) cortices, left superior parietal lobe (SPL), and right parahippocampal gyrus (Parahip). (B) NBS analysis revealed a single network of decreased FC in patient controls as compared with healthy controls (p = 0.03, FWER) comprising a total of 33 nodes connected by 39 edges and including several nodes located in the somatosensory-motor (M1 and S1) and occipital regions, midcingulate cortex (MCC), posterior IC, left MTG, and inferior parietal lobe (IPL) and SPL. (C) NBS analysis revealed two subnetworks of decreased FC in relatives of suicide victims as compared with healthy controls. The first subnetwork (p = 0.001, FWER) comprised a total of 61 nodes connected by 118 edges and included several occipital, temporal and somatosensory-motor regions, bilateral IFG, parahippocampal gyrus, right posterior IC, left IPL, bilateral angular gyrus (AnG), and precuneus (PreC). The second subnetwork (p = 0.02, FWER) comprised a total of 21 nodes connected by 26 edges and included bilateral putamen (Put), bilateral anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (DMPFC), bilateral supplementary motor area (SMA), right premotor cortex (pM), bilateral thalamus (Thal), right STG, and right hippocampus (Hipp). (D) NBS analysis revealed a single network of decreased FC in relatives of suicide victims as compared with relatives of patients with no family history of suicidal behavior (p = 0.02, FWER) comprising a total of 26 nodes connected by 28 edges and including somatosensory-motor regions, ACC and MCC, right IFG, right posterior IC, bilateral thalamus, bilateral STG, and right MTG, left SPL, left fusiform gyrus and middle occipital gyrus (OCx).