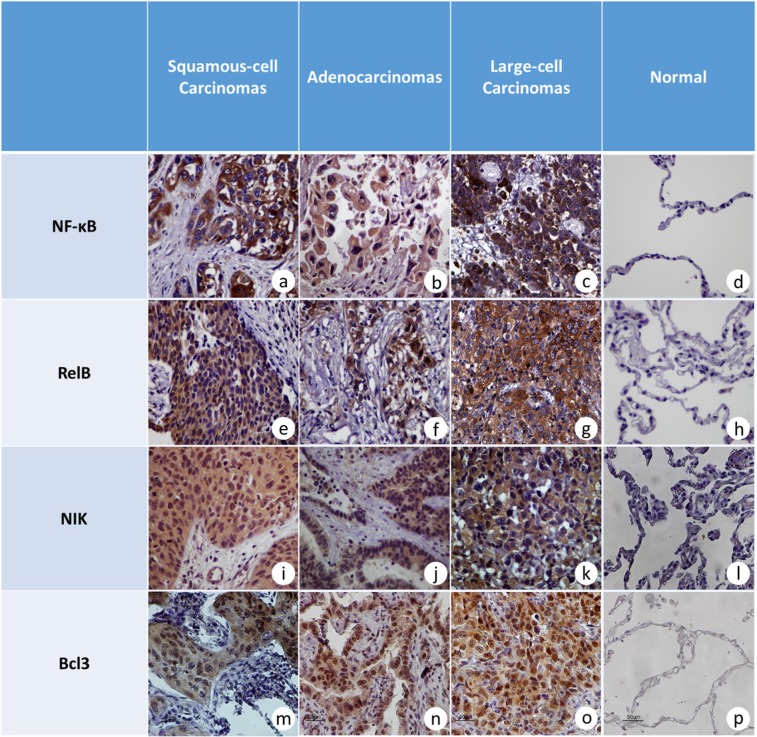
Figure 2.
Microphotographs (×40) from tumor and tumor-adjacent, non-cancerous samples. (a) NF-κB2 in a grade II, squamous lung carcinoma with strong and intermediate cytoplasmic staining without nuclear signal, (b) NF-κB2 intermediate cytoplasmic staining in adenocarcinoma, (c) strong and intermediate cytoplasmic signal for NF-κB2 in an undifferentiated large-cell carcinoma, (d) negative immunostaining for NF-κB2 protein in alveolar epithelium and interstitium of tumor-adjacent non-neoplastic lung parenchyma, (e) RelB immunodetection in a grade III, squamous-cell carcinoma with strong cytoplasmic staining, (f) strong nuclear and cytoplasmic staining for RelB protein in grade III lung adenocarcinoma, (g) representative section of undifferentiated large-cell, lung carcinoma with strong cytoplasmic signal for RelB, (h) negative immunostaining for RelB in alveolar epithelium and interstitium of tumor-adjacent non-neoplastic lung parenchyma from a squamous-cell carcinoma, (i) representative section from a grade I, squamous -cell carcinoma with strong cytoplasmic staining for NIK, (j) intermediate cytoplasmic staining for NIK in an adenocarcinoma, (k) strong cytoplasmic immunostaining for NIK in large-cell lung carcinoma, (l) negative immunostaining for ΝΙΚ in alveolar epithelium and interstitium of adjacent non-neoplastic lung parenchyma from a large-cell carcinoma, (m) representative section of grade I, squamous-cell carcinoma with strong cytoplasmic and intermediate nuclear staining for Bcl3, (n) strong cytoplasmic staining for Bcl3 in a lung adenocarcinoma, (o) intermediate nuclear and strong cytoplasmic staining for Bcl3 protein in a large-cell lung carcinoma, (p) negative immunostaining for Bcl3 in alveolar epithelium of tumor-adjacent, non-neoplastic lung parenchyma.