Figure 5.
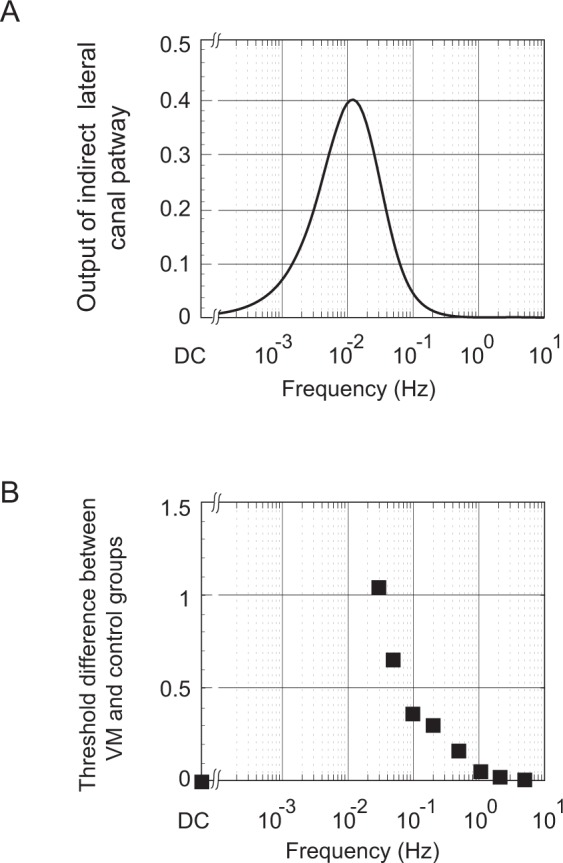
Comparison of frequency-dependence of velocity storage and vestibular migraine thresholds. (A) Frequency-dependence of the “indirect” velocity storage pathway (simulated with the Raphan and Strum model52) using the TVS measured in VM patients (20.9 s) and an arbitrary gain value. The combination of the canal high-pass filter and the velocity storage low-pass filter in series yields an output that peaks between the canal and velocity storage cut-off frequencies (approximately 0.03 Hz and 0.01 Hz respectively). (B) Threshold abnormality in VM patients to roll tilt stimuli (VM threshold – [non-VM] threshold) for each frequency, using geometric means, including the “quasi-static DC” results13,28.
