Fig. 3.
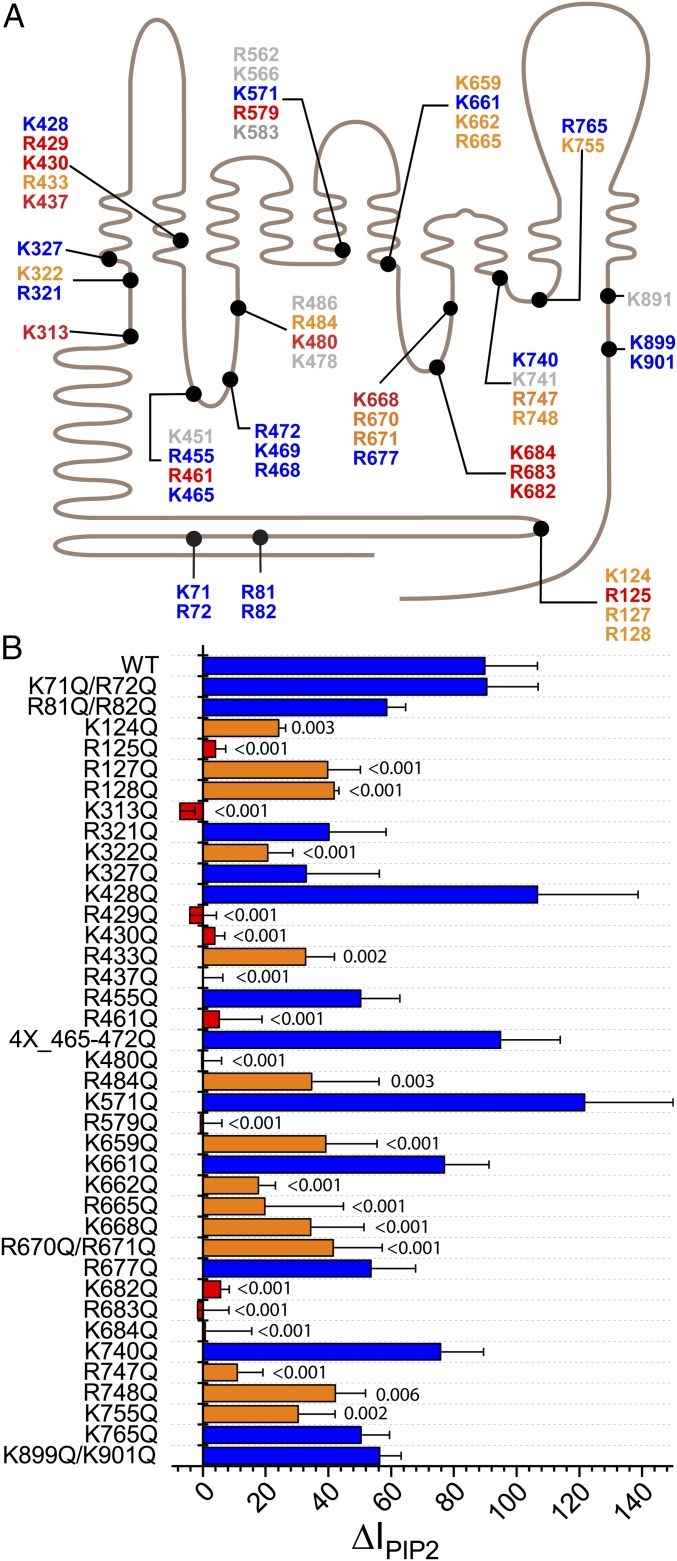
Amino acids involved in mediating the effect PI(4,5)P2 on ANO1. (A) Schematic of 51 basic amino acids that were considered potential PI(4,5)P2 interacting residues. ANO1 is represented as a line with 10 transmembrane helices. Extracellular is upward. The length of the line is scaled to the amino acid sequence. Colors indicate effect of mutagenesis on stimulation of ANO1 current by PI(4,5)P2 corresponding to B: blue, response was like WT; red, PI(4,5)P2 effect was essentially abolished; orange, PI(4,5)P2 effect was significantly reduced; gray, not tested. (B) Effects of mutation of basic amino acids in ANO1 on the stimulation of ANO1 current in inside-out patches by PI(4,5)P2. Ten micromolar PI(4,5)P2 stimulates WT ANO1 current by ΔIPIP2 = 89.9%. Error bars are ±SEM; n = 3 to 13 patches per mutation. Numbers above bars show statistical P calculated by one-way ANOVA with Fisher LSD post hoc analysis for difference between means. Blue bars: P > 0.05. Orange bars: P < 0.05 and >50% reduction in response to PI(4,5)P2. Red bars: P < 0.01 and >90% reduction in response to PI(4,5)P2.