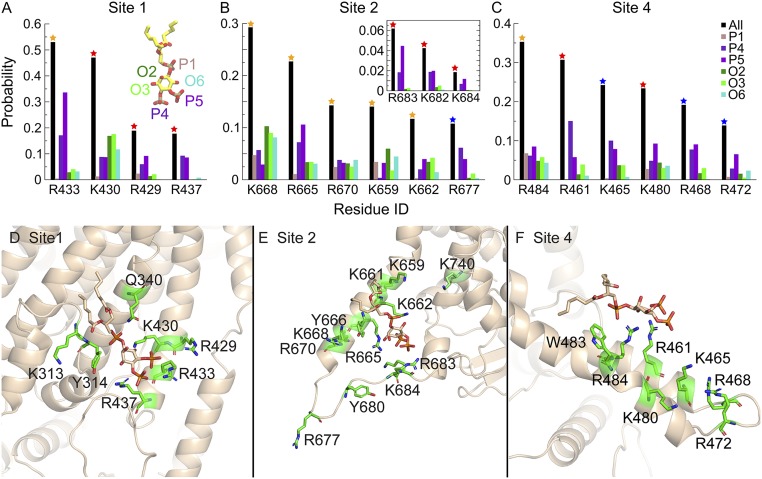
Fig. 7.
PI(4,5)P2 coordination in major binding sites. (A–C) The probability of C6-PI(4,5)P2 headgroup coordination by the key basic residues in sites 1, 2, and 4 is shown as black bars. Residues that coordinate C6-PI(4,5)P2 for >10% of the total binding time in each site are shown [other residues that affect PI(4,5)P2 binding experimentally are also shown in the Inset]. The color of the star on each bar represents the experimental results in Fig. 3B, where the mutation of the residues affects PI(4,5)P2 binding to different degrees. The coordination probability for each functional group on the inositol ring (1′-phosphate, 4′-phosphate, 5′-phosphate, 2′-hydroxyl, 3′-hydroxyl, and 6′-hydroxyl) is shown individually. (D–F) Coordination of C6-PI(4,5)P2 in sites 1, 2, and 4. Amino acids that interact with each binding site are shown as stick representation in green. PI(4,5)P2 is shown in stick representation in tan.