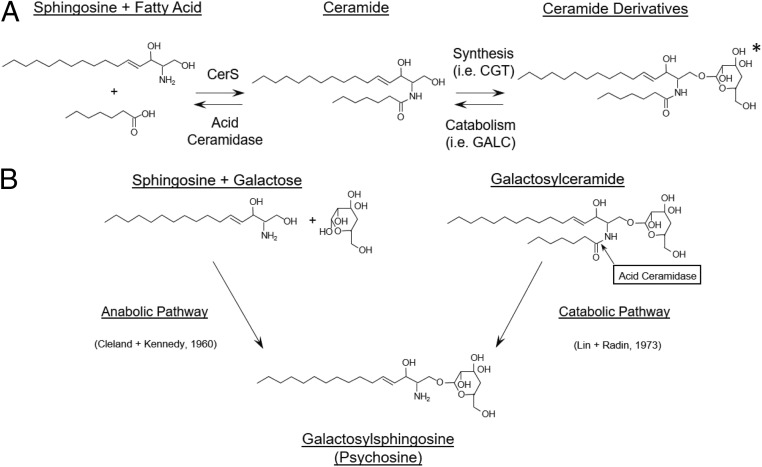
Fig. 1.
Role of ACDase in ceramide degradation and psychosine synthesis. (A) ACDase is responsible for the lysosomal degradation of ceramides originating from various cellular sphingolipid sources. The ceramide derivative shown is galactosylceramide (the asterisk [*] indicates that galactose can be substituted by sulfated galactose, glucose, sialic acid, oligosaccharides, phosphocholine, or phosphate residues; synthesized; and catabolized by other enzymes). CerS and CGT are abbreviations for ceramide synthase and ceramide galactosyltransferase, respectively. (B) Psychosine can potentially be synthesized either through the anabolic dehydration of sphingosine and galactose (Left) or through the catabolic deacylation of galactosylceramide by acid ceramidase (Right). Two studies have directly (5) or indirectly (6) supported the anabolic pathway.