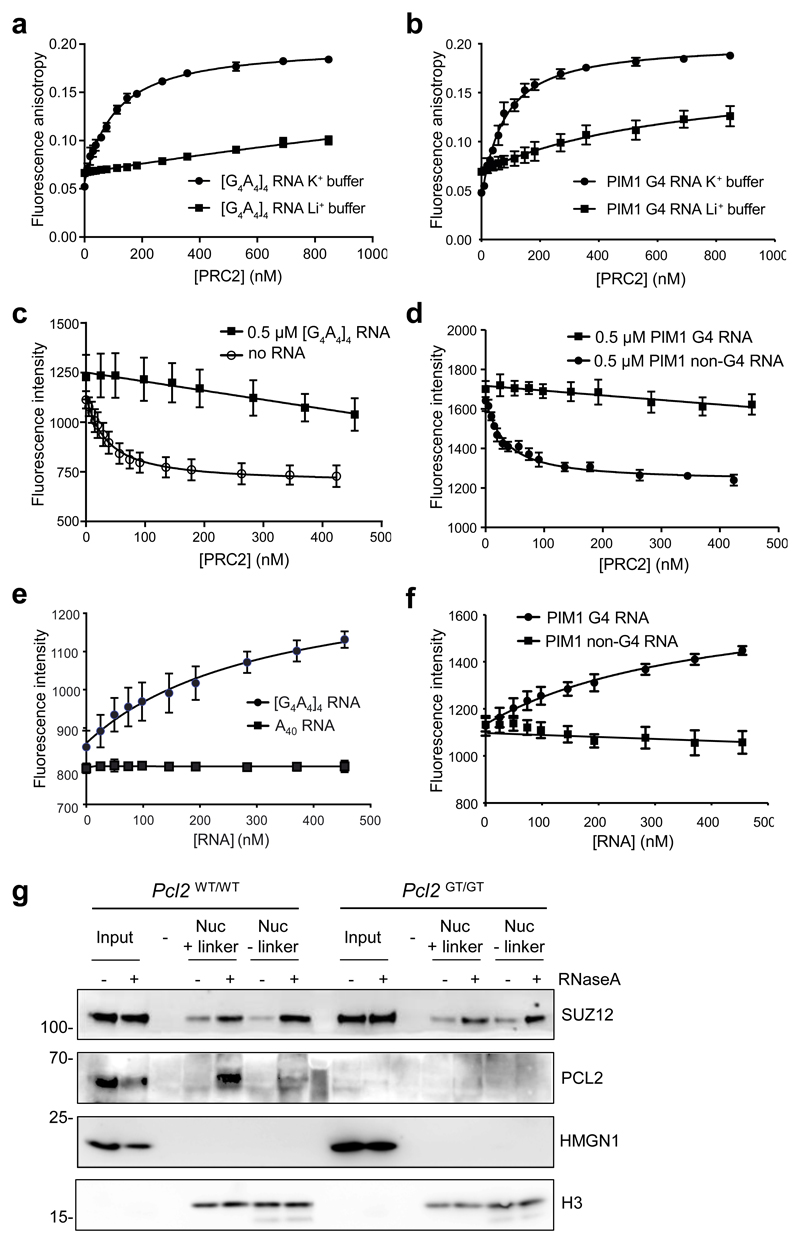
Fig. 3. G4 RNA inhibits interaction of the PRC2 catalytic core with the substrate core nucleosome particle.
(a) Fluorescence anisotropy measuring binding of the PRC2 catalytic core (EZH2–EED–SUZ12 VEFS domain) directly to fluorescein labelled [G4A4]4 RNA in either 100 mM K+ or Li + buffer (mean and S.E., n=3 independent experiments).
(b) As (a) except for the 24 nt G4-forming sequence within PIM1 RNA.
(c) Fluorescence intensity measuring binding of the PRC2 catalytic core directly to MDCC-labeled H3K27M obligate substrate core nucleosome particles (reconstituted with 147 bp DNA) in the presence of 500 nM [G4A4]4 RNA or no RNA (mean and S.E., n=3 independent experiments).
(d) As (c), except with 500 nM PIM1 G4 RNA or a control non-G4-forming 24 nt portion of PIM1 RNA.
(e) Titration of [G4A4]4 and control A40 RNAs into a pre-formed complex of core PRC2 and MDCC-labeled substrate core nucleosome particle. The increase in fluorescence intensity with [G4A4]4 RNA is interpreted as release of PRC2 from the nucleosome (mean and S.E., n=3 independent experiments).
(f) As (e), except with G4 and non-G4 forming PIM1 RNAs.
(g) Immunoblot for SUZ12, PCL2, HMGN1 and H3 after co-immunoprecipitation of PRC2 from Pcl2GT/GT or Pcl2WT/WT ESC with nucleosomes containing biotin-tagged histone H2A (reconstituted with either 185 bp or 147 bp DNA) from mock or RNaseA-treated nuclear extract. Representative of 2 independent experiments. Uncropped blot images are shown in Supplementary Data Set 1.