Figure 1.
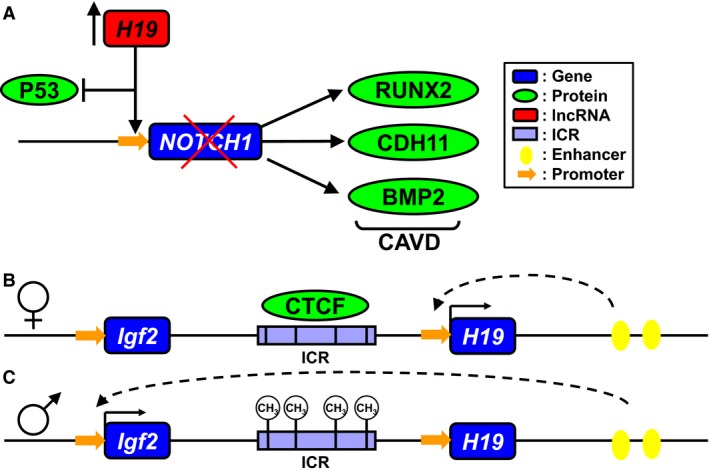
H19 imprinting and effect on CAVD. (A) High levels of H19 compete with P53 to bind the NOTCH1 promoter, decreasing expression of NOTCH1 and mimicking a loss‐of‐function mutation known to lead to CAVD. The H19/IGF2 locus contains a differentially methylated domain in the intergenic space. On the maternally inherited allele (B) CTCF binds to a series of four 21bp repeats, resulting in interaction of downstream enhancers with the H19 promoter and expression of H19. CTCF also acts as an insulator, keeping the downstream enhancers from promoting Igf2 expression. On the paternal allele (C) methylation of the differentially methylated domain prevents CTCF from binding, enabling enhancer interaction with the IGF2 promoter. IGF2 expression is increased, while H19 expression is almost entirely stopped. Hypomethylation in the ICR can lead to increased H19 expression
