Figure 5.
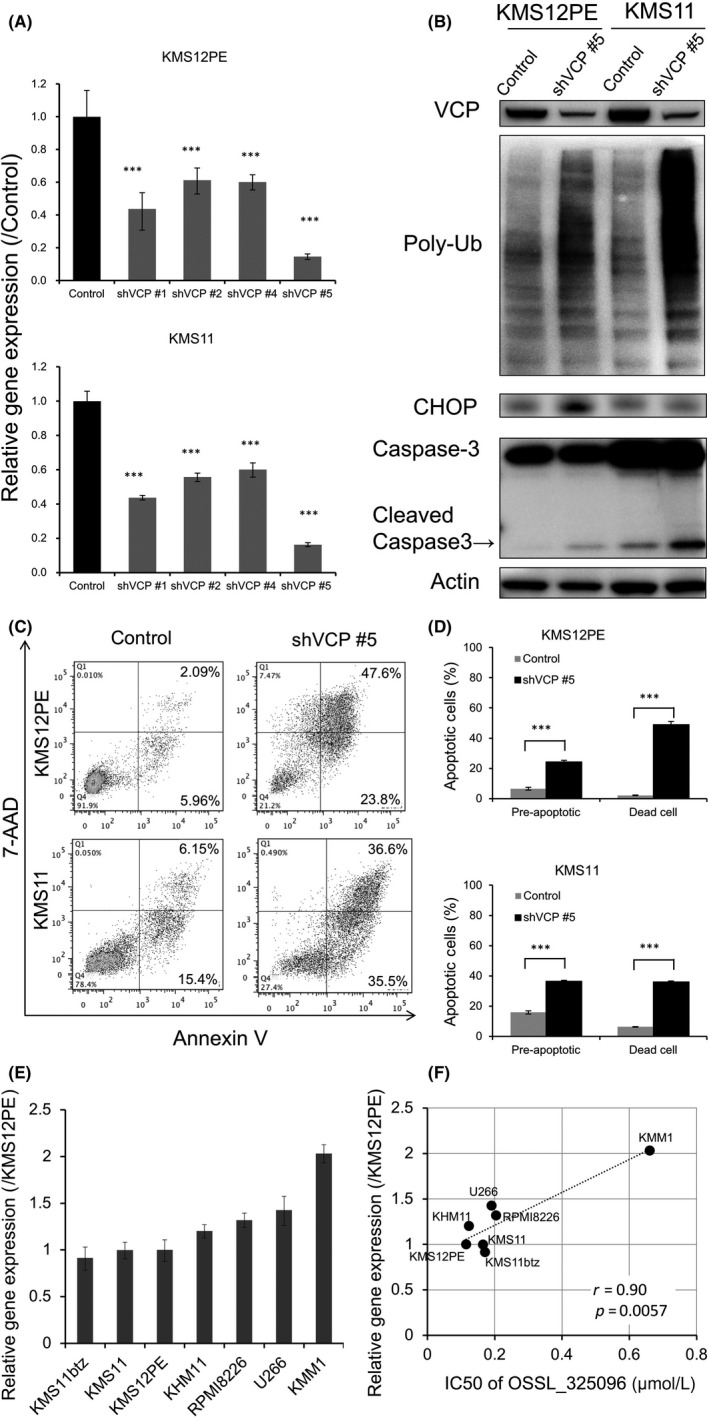
Knockdown of VCP induces accumulation of endoplasmic reticulum‐associated protein degradation (ERAD)‐associated proteins and apoptosis in multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines. shRNA‐mediated knockdown of VCP was carried out in MM cell lines. KMS12PE or KMS11 cells were stably transfected with tetracycline‐inducible shRNA plasmids, and shRNAs were induced by exposure of 1 μmol/L doxycycline for 48 h. Non‐targeting shRNA served as a control. A, Knockdown efficacies were determined by RT‐qPCR after shRNA induction in KMS12PE and KMS11 cells. shVCP#5 induced the strongest knockdown of VCP mRNA levels to <20% of that with control shRNA. Data represent mean ± SD derived from three separate experiments. B, Western blotting for VCP, poly‐ubiquitinated protein (Poly‐Ub), CHOP, and caspase‐3 in KMS12PE and KMS11 cells was carried out after shVCP#5 induction. Along with knockdown of p97/VCP protein, poly‐ubiquitinated protein accumulated and caspase‐3 was cleaved in KMS12PE and KMS11 cells. C, Dot plots and D, bar charts of MM cells stained with annexin V and 7AAD after shVCP#5 induction. VCP knockdown induced apoptosis in KMS12PE and KMS11 cells. Data represent the mean ± SD derived from three separate experiments. Significance values are indicated as ***P < .001 (Student's t‐test). E, Expression levels of VCP in myeloma cell lines. Real‐time PCR of VCP was carried out with myeloma cell lines. β‐Actin expression levels were used for standardization of VCP expression levels. F, Dot plot graph of VCP expression levels and IC 50 of OSSL_325096 in myeloma cell lines is shown. Significance values are indicated as P‐value
