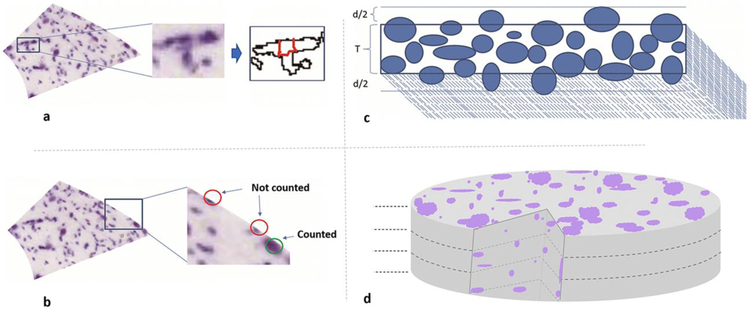
Fig. 2.
Computing cell counts from segmented object: a. Segmentations were de-clumped using the watershed algorithm (illustrated section: 70_CA2SLM). b. Bordering cells were sorted based on cell area and only upper half was counted for that section while lower half was considered to belong to neighboring areas. c. Cut cells due to sectioning were accounted for using Abercrombie formula: , where N is the number of cells after correction, n is the number of all detected objects before correction, T is the section thickness, and d is the mean diameter. d. Section thickness is divided into equal layers where height of each layer equals mean cell diameter; occcluded cells in the depth of the tissue were accounted for using the formula for count estimates of aligned particles (see Methods). Figure was created using ImageJ, Microsoft PowerPoint and Adobe Photoshop