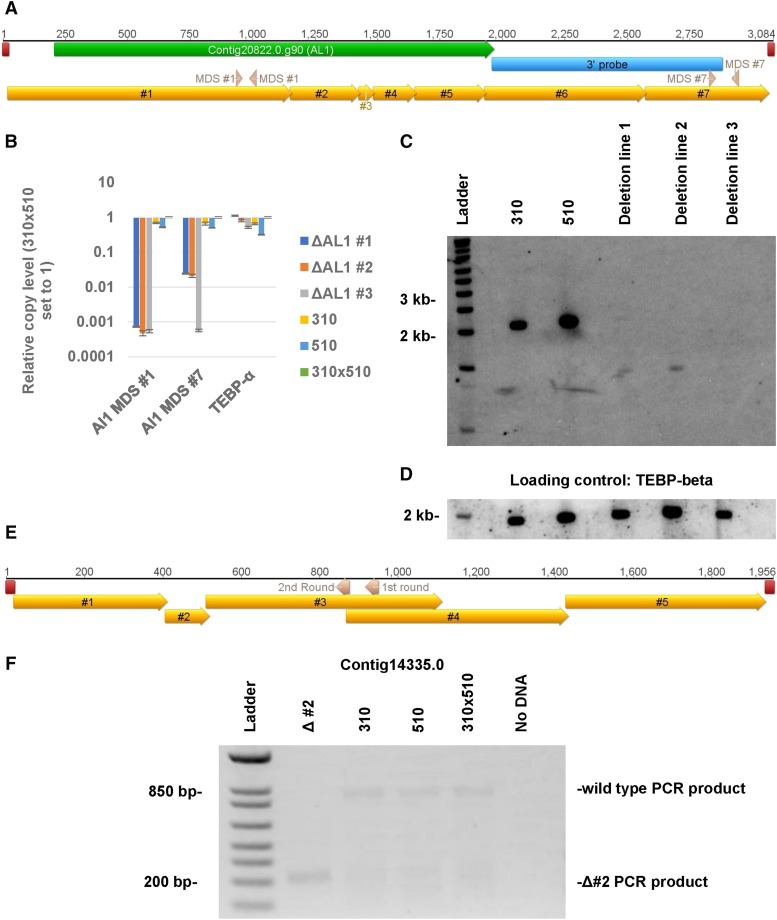
Figure 3.
Remnants of deleted chromosomes are detected in some of the deletion lines. A) A diagram of the AL1 nanochromosome with various features labeled, including the locations of the telomeres (red), the AL1 gene (green), the MDSs (gold), the qPCR primers (pink, labeled with which qPCR they belong to in panel B, and hybridization region of the Southern probe (blue). B) Quantification of the 3′ and 5′ end of the chromosome via qPCR and the relative copy vs. the JRB310xJRB510 F1 genomic DNA. Error bars represent the standard deviation. C) Southern analysis of the first 3 contig20822.0 (AL1) deletion lines (#1, #2, and #3) using a probe against the 3′ end of the nanochromosome. D) The same membrane was then stripped and re-probed with TEBP-beta for loading control. E) A depiction of the contig14335.0 nanochromosome with MDSs (gold), telomeres (red), and the gene specific primers for the two rounds of telomeric PCR (pink, labeled with which PCR round they are involved in) labeled. F) Second round of telomeric PCR (see methods for description of telomeric PCR) for the 5′ end of the Contig14335.0 chromosome in contig14335.0 deletion line #2. Telomeric PCR products from contig14335.0 deletion line #2 were Sanger sequenced to identify the exact location of the aberrant telomere addition (see supplementary figure 6).