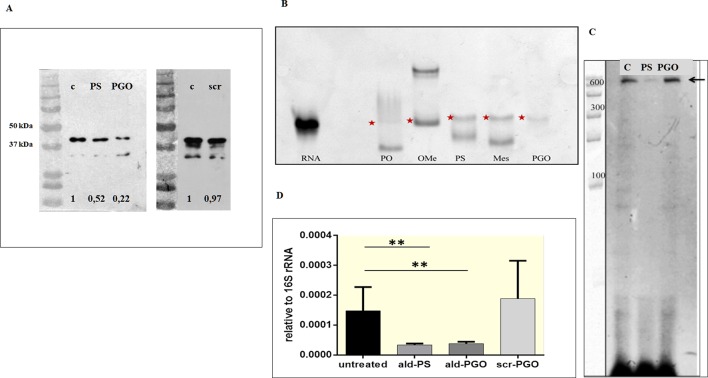
Figure 3.
2′-OMe PGO inhibits the expression of the target gene in Mycobacterium smegmatis. (A) Specific inhibition of protein synthesis by antisense ald-PGO. M. smegmatis cultures were treated with 20 μM of ald-PGO (PGO), ald-PS (PS), and scr-PGO (scr) or left untreated (control, C) for 24 h and analyzed for Ald protein expression by western blotting; numbers below indicate the ratio to control. (B) Cleavage of ASO : RNA duplexes by RNase H. Target RNA duplexes with ald (PO), ald-oligo-2′-O-methylribonucleotide (OMe), ald-PS (PS), μ-ald (Mes), and ald-PGO (PGO) were treated by RNAse H and analyzed by PAGE in a denaturing 15% gel, which was stained with SYBR Green. Red asterisks indicate RNA. (C) Primer extension analysis of the ald gene transcription. RNA was isolated from M. smegmatis cultures treated with 20 μM of ald-PGO (PGO) and ald-PS (PS) or left untreated (control, C) for 24 h and reverse transcribed using a radioactively labeled ald-specific oligonucleotide. The arrow indicates the transcription start point. RiboRuler RNA ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific) is shown at the left. (D) Quantification of ald transcription. M. smegmatis cultures were treated with 20 μM of the indicated ASOs for 24 h and analyzed for ald mRNA expression by qRT-PCR. The data are normalized to the 16S rRNA transcription level. **p < 0.01. 2′-OMe PGO, phosphoryl guanidine oligo-2′-O-methylribonucleotide; PAGE, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction