Figure 1.
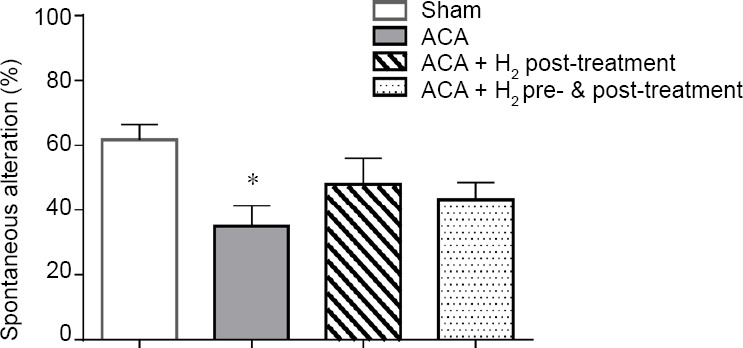
Effect of hydrogen (H2) treatment on the T-maze test of rats with asphyxia induced-cardiac arrest (ACA) at 7 days post-resusciation.
Note: Rats subjected to ACA had significantly lower rates of spontaneous alteration between the right and left arms than shams. There was a tendency toward improved T-maze performance in ACA rats that received hydrogen gas pre&post-treatment. Data were presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 6/group). *P < 0.05, vs. sham group (one-way analysis of variance followed by Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test).
