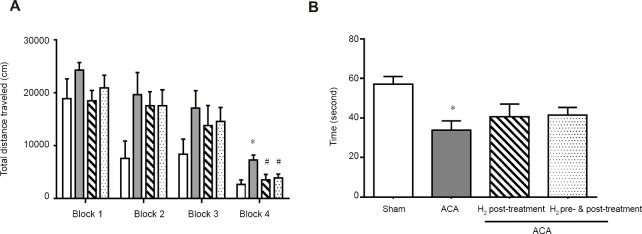
Figure 2.
Effect of hydrogen (H2) treatment on the Morris water maze test of rats with asphyxia induced-cardiac arrest (ACA) starting at 14 days post-resuscitation.
Note: (A) Swimming distance. There were signficant longer swimming distances in rats subjected to ACA at the 4th day of spatial learning testing. H2 treatment significantly shortened the total swimming distance. (B) Latency. Probe test showed that rats subjected to ACA spent significantly lesser time than shams in the quadrant where the platform was placed during spatial learning testing. This effect was diminished by H2 treatments. Data were presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 6/group). *P < 0.05, vs. sham group; #P < 0.05, vs. ACA group (one-way analysis of variance followed by Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test).