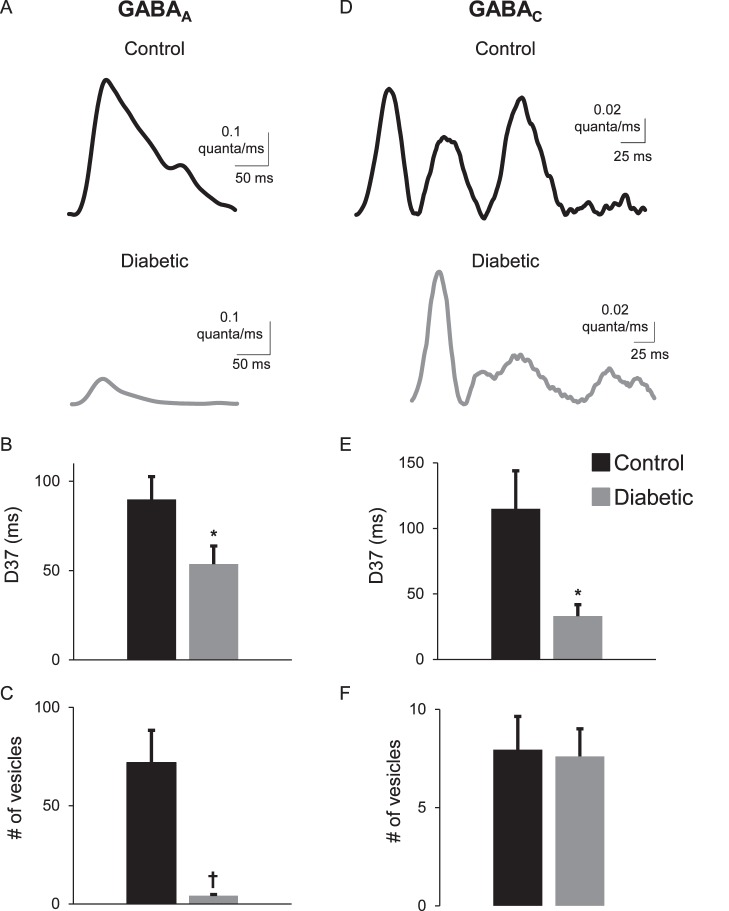
Figure 5.
GABA release from A17 amacrine cells is decreased after 6 weeks of diabetes. (A, D) GABA release was estimated using deconvolution of an average GABAAR and GABACR spontaneous IPSC with the corresponding receptor fIPSC from the control and diabetic rod bipolar cells in Figure 4. Representative traces of the timecourse of GABA release from A17 amacrine cells onto rod bipolar cell GABAARs (A) and GABACRs (D) show that timecourse of GABA release was shortened under diabetic conditions. (B, E) The average D37 of vesicle release was faster in diabetic cells for GABA release onto GABAARs (n = 11 cells, P = 0.04 t-test) and GABACR (n = 9 cells, P = 0.02 t-test). (C, F) The amount of vesicle release onto GABAARs (C) was significantly reduced (P = 0.001), but vesicle release onto GABACRs (F) was not different (P = 0.9). *P < 0.05, †P < 0.01.