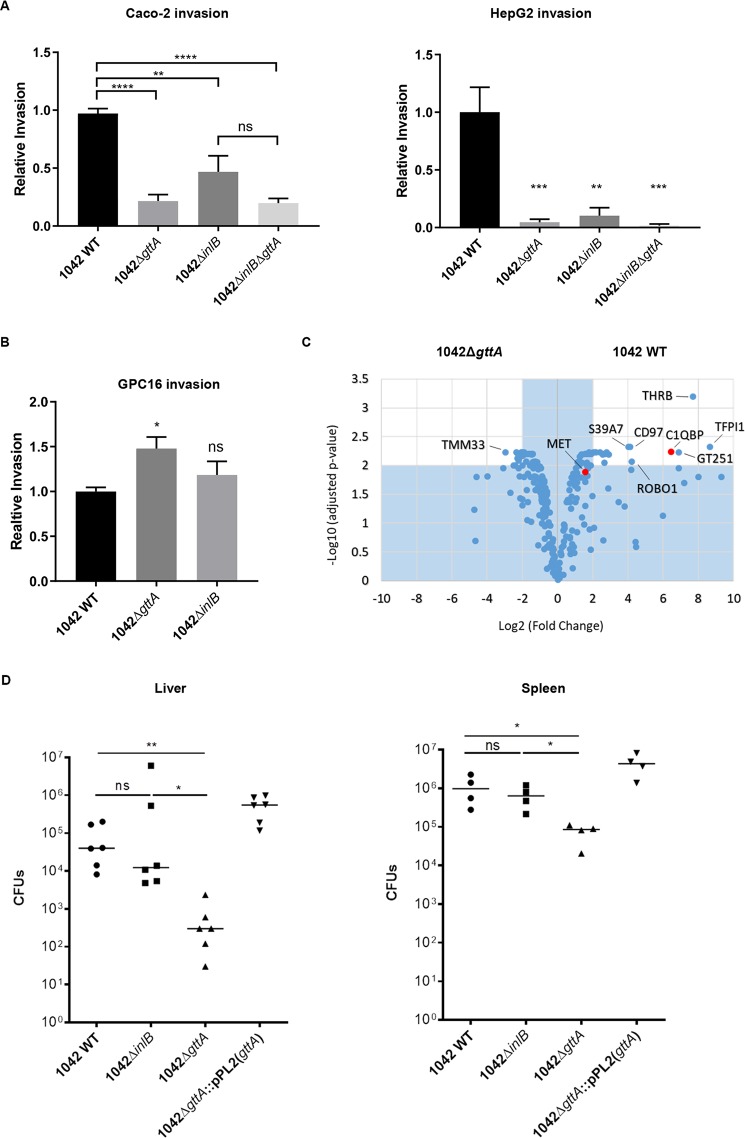
Fig 5. Galactosylated teichoic acids are required for cMet/gC1qR-mediated invasion and virulence.
(A) Relative invasion of the indicated strains to 1042 WT following a three-hour infection of Caco-2 and HepG2 cells (mean ± SEM; for HepG2, n = 3; for Caco-2, n = 5; ****P<0.0001; ***P<0.001; **P<0.01, as determined by a one-way ANOVA; ns, not significant, as determined by a student’s t-test). (B) Relative invasion of the indicated strains to 1042 WT following infection of GPC16 cells (mean ± SEM; n = 6 from two individual experiments; *P<0.05; ns, not significant relative to WT). (C) HATRIC-LRC identification of target receptors of 1042 WT and 1042ΔgttA on the surface of HeLa cells. Relative fold changes of proteins (Log2 scale) are plotted against their respective log-transformed, false-discovery rate (FDR)-adjusted values. Target receptors are defined as proteins with a fold change greater than 4 and p-value less than or equal to 0.01, corresponding to the white space of the plot. Known receptors recognized by InlB are shown in red. (D) Bacterial burden in spleen and liver upon intravenous injection of L. monocytogenes and isogenic mutants. C57BL/6J mice were intravenously injected with 5x103 CFUs/animal and dissected 3 days post infection. Values represent the number of CFUs per organ. One dot represents one animal; horizontal bar the median. Mann-Whitney tests were performed to determine statistical significance. **P<0.01, *P<0.05.