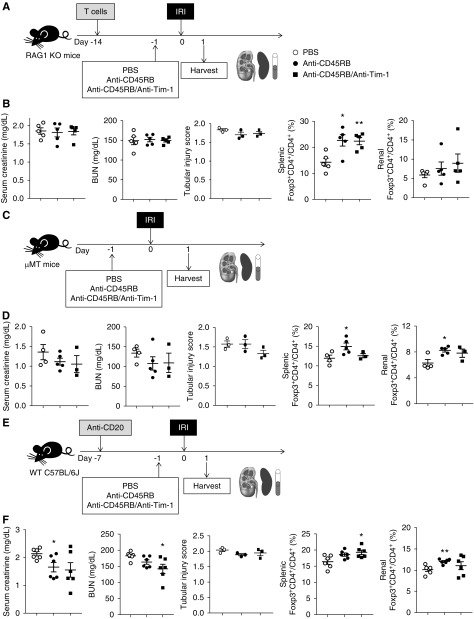
Figure 7.
B cells were indispensable in the reno-protective effects of anti-CD45RB with or without anti–Tim-1 treatment against IRI. (A) T cells from WT mice were transferred to RAG1 KO mice 2 weeks before IRI. Anti-CD45RB, anti-CD45RB with anti–Tim-1, or PBS was administered to RAG1 KO mice with transferred T cells 1 day before IRI; mice were harvested on 1 day after IRI. (B) Levels of serum creatinine and BUN. Flow cytometry analysis of splenic and renal Tregs in RAG1 KO mice. (C) Anti-CD45RB, anti-CD45RB with anti–Tim-1, or PBS was administered to μMT mice 1 day before IRI; mice were harvested 1 day after IRI. (D) Levels of serum creatinine and BUN. Flow cytometry analysis of splenic and renal Tregs in μMT mice. (E) Anti-CD20 was administered to WT mice to deplete B cells 1 week before IRI. Anti-CD45RB, anti-CD45RB with anti–Tim-1, or PBS were administered 1 day before IRI; mice were harvested 1 day after IRI. (F) Levels of serum creatinine and BUN. Flow cytometry analysis of splenic and renal Tregs in WT mice with B cell depletion. Results were expressed as dot plots with the mean±SEM. n=6. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with the PBS group. IRI, ischemia-reperfusion injury; KO, knockout; RAG1, recombination activating gene 1; Tregs, regulatory T cells; WT, wild type.