Figure 8.
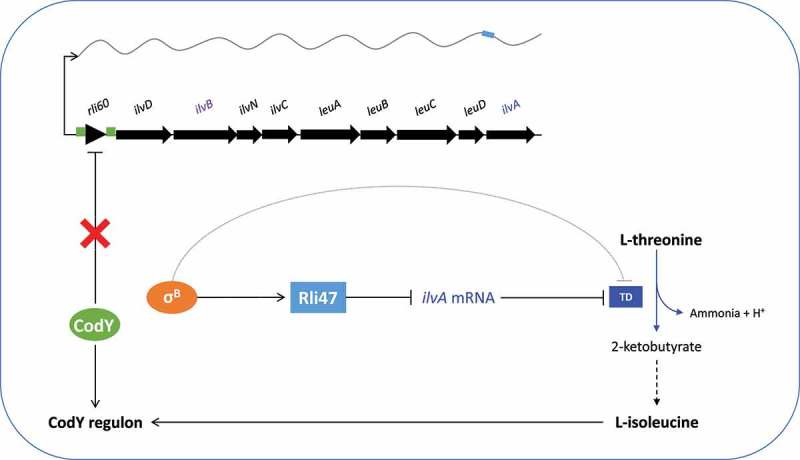
Proposed model of the regulatory effect of Rli47 on isoleucine biosynthesis in L. monocytogenes. Transcription of rli47 is under σB control and when it is expressed it interacts directly with mRNA from the ilv-leu operon at the predicted Shine-Dalgarno sequence upstream from the ilvA start codon. The Rli47-ilv interaction blocks the first step of isoleucine biosynthesis by preventing the translation of ilvA to produce threonine deaminase (TD), and also by affecting the stability of the ilv-leu transcript. σB negatively influences the activity of TD through an Rli47-independent route which remains to be identified. CodY represses transcription of the ilv-leu operon in a manner that depends on the availability of isoleucine (ile) through an interaction with two binding sites, shown in green [10,12]. When σB is active Rli47 influences the CodY regulon through an effect on the cytoplasmic pool of isoleucine.
