Figure 7.
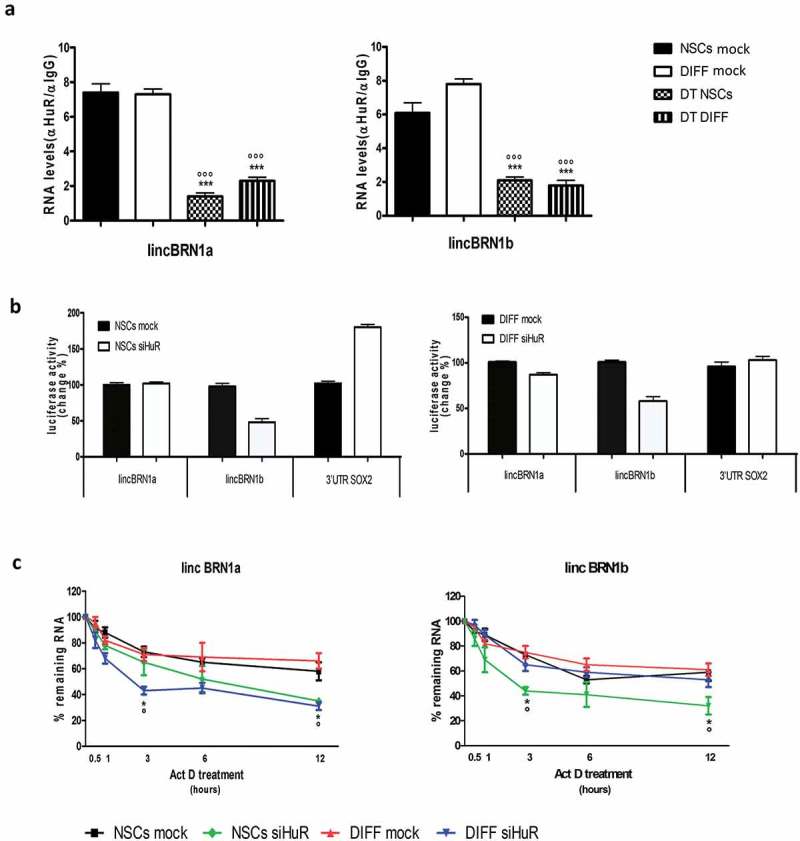
Investigation of the interaction between HuR and lincBRN1a/lincBRN1b.
(a). RNA immunoprecipitation assay (RIP) for HuR was performed in neurospheres (NSCs) and at the end of the 8-day differentiation process (DIFF). Cells were analyzed in the presence or absence of dihydrotanshinone (DT 1µM), an RNA-HuR interaction interfering agent. LncRNAs lincBRN1a and lincBRN1b show a strong affinity for the HuR antibody-coated beads and DT destroys this interaction, indicating a specific interaction between the RNA-binding protein and the lncRNAs. Quantification was performed by Real time PCR and quantification was expressed with reference to the input. Results are expressed as the mean of three different experiments ± SD (*** p < 0.001 vs NSCs; °°° p < 0.001 vs DIFF; with n = 3). (b). Luciferase reporter assay performed on NSCs and differentiated cells (DIFF) in the presence or absence of siHuR. The experiment was performed transfecting reporter plasmids carrying AU-rich regulatory regions of lincBRN1a and lincBRN1b, 3ʹUTR SOX2 reporter was used as positive control. Results are expressed as the mean of three different experiments ± SD. (c). RNA turnover assay. The lncRNAs expression levels (lincBRN1a and lincBRN1b) were monitored at 30 min, 1, 3, 6 and 12 h after the administration of Actinomycin D in presence or absence of HuR silencing (siHuR). Results are expressed as the mean of three different experiments ± SD (*p < 0.05 vs NSCs MOCK; ° p < 0.05 vs DIFF MOCK; with n = 3).
