Figure 2.
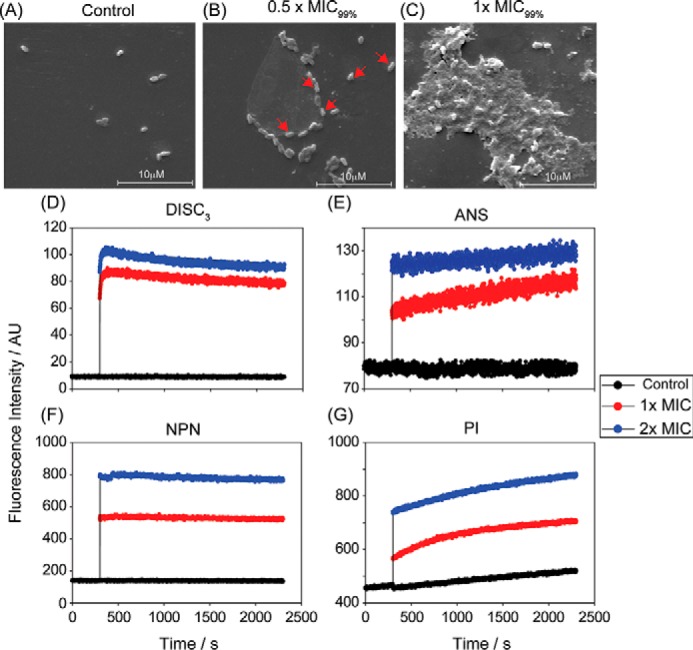
A, SEM images of X. vesicatoria in the absence of both the peptides VG16KRKP and KYE28 (control) showed no visible morphological changes after 1 h of incubation. In contrast, cells exposed to 0.5 × MIC99% (MIC99% = 1 μm each) showed onset of cell distortion (B), and exposure at 1× MIC99% resulted in pronounced membrane perturbation with extensive release of intracellular constituents and loss of cellular morphology (C). The scale corresponds to 10 μm. Additionally, dye-based fluorescence assay with live X. vesicatoria cells displayed that the peptide combination at 1× and 2× MIC99% concentration could effectively interact with bacterial cell membrane bringing about a change in membrane potential as indicated by an increase in DISC3 fluorescence (D), thus disrupting the outer membrane comprising of lipopolysaccharide (E and F), and the inner membrane made of negatively charged lipid components (G). The control cell showed baseline fluorescence under all conditions. It should be noted that ANS and NPN are lipophilic dyes, which fluoresces strongly in nonpolar environments of the cell membrane, which gets exposed upon membrane disintegration. PI, however, binds to nucleic acid components of the dead cell conforming inner membrane disruption. Each experiment was recorded for 30 min at 298 K.
