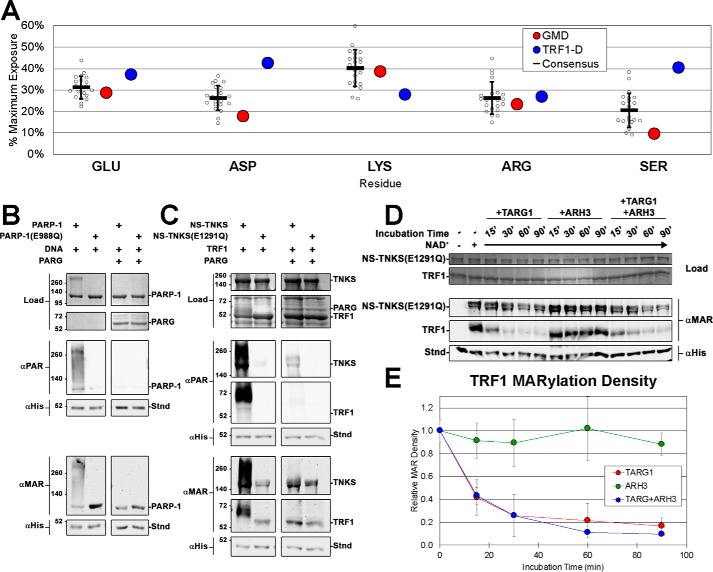
Figure 7.
TNKS as a glutamate-targeting PARP in vitro. A, solvent accessibility of common PARylated residues in TRF1-D (DNA-binding domain) and GMD crystal structures compared with a consensus residue exposure derived from a collection of homomultimeric crystal structures (see Table S1). B and C, activity assays examining the effects of PARG treatment of PAR/MAR-modified PARP-1 (B) and PAR/MAR-modified NS-TNKS with TRF1 (C). PARP-1 constructs consisted of WT PARP-1 and NS-TNKS as well as mutants PARP-1(E988Q) and NS-TNKS(E1291Q) that are confirmed to primarily synthesize MAR. The designated reaction mixtures were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (Load) and by Western blot analysis of PARylation (αPAR) and MARylation (αMAR). A His-tagged protein (Stnd) was added to each reaction after quenching to assess transfer efficiency of the blot; the protein was detected with an anti-His antibody (αHis). D, NS-TNKS(E1291Q) and TRF1 were mixed, incubated for 30 min (with or without NAD as indicated), and then quenched by the addition of PARP inhibitor rucaparib. MAR-modified NS-TNKS(E1291Q) was then treated with the hydrolases TARG1 and ARH3 (alone and in combination) over a time course to measure their ability to remove MAR. Reactions were quenched by the addition of Laemmli sample buffer. The designated reaction mixtures were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (Load) and by Western blot analysis of MARylation (αMAR). A His-tagged protein (Stnd) was added to each reaction after quenching to assess transfer efficiency of the blot; the protein was detected with an anti-His antibody (αHis). See Fig. S9, D and E, for the complete SDS-PAGE and Western blot images. E, quantification of the TRF1 band intensity from D. Quantification of the band intensity of NS-TNKS(E1291Q) is shown in Fig. S9A. Data represent the mean, error bars represent S.D.