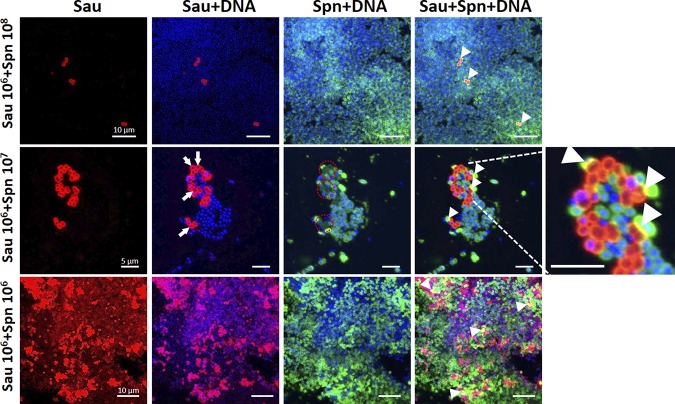
FIG 2.
S. pneumoniae (Spn) contact-dependent killing of S. aureus (Sau) induces loss of DNA signal. Bacteria growing on blood agar plates from the experiments presented in Fig. 1, inoculated with the specific density of each species shown on the left, were imprinted onto glass slides. The preparations were fixed with paraformaldehyde, and S. aureus bacteria were stained with an anti-S. aureus antibody followed by an anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 555-labeled antibody. S. pneumoniae was stained with an Alexa Fluor 488-labeled anti-S. pneumoniae antibody, while the DNA was stained with DAPI. The preparations were analyzed with a confocal microscope. Shown are 3D reconstructions of z stacks obtained from xy optical sections. The specific channel of each panel is shown at the top. The arrows point to S. aureus bacteria stained red with a loss of DNA signal, while the red dashed circles indicate areas where DNA signal is missing, corresponding to the arrows. The arrowheads show physical colocalization (yellow) of S. aureus and S. pneumoniae. The dimensions of the scale bars shown in the left column apply to all the images in the same row. The image on the far right was digitally enlarged to show details of the area indicated by the dashed lines.