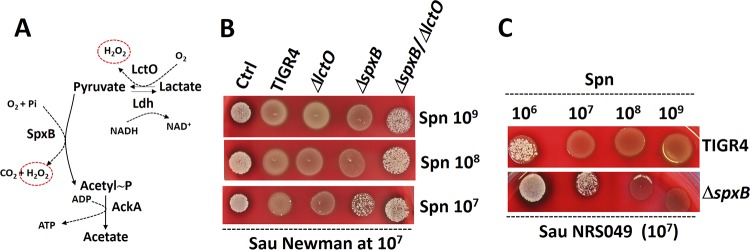
FIG 5.
S. pneumoniae (Spn) contact-mediated killing of S. aureus (Sau) requires enzymes SpxB and LctO. (A) Oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl∼P by the enzyme pyruvate oxidase (SpxB). The reaction uses molecular O2 and inorganic phosphate (Pi), producing CO2 and H2O2 (circled). Acetyl∼P is then converted to acetyl coenzyme A by acetate kinase (AckA) in a reaction that produces ATP. The enzyme lactate oxidase (LctO) catalyzes the formation of pyruvate from lactate, producing H2O2. (B) S. pneumoniae strains TIGR4, TIGR4 ΔlctO, TIGR4 ΔspxB, and TIGR4 ΔspxB ΔlctO were inoculated on blood agar plates at the densities indicated on the right (CFU per milliliter) concurrently with S. aureus strain Newman, which was inoculated at a density of ∼107 CFU/ml. (C) S. pneumoniae strains were inoculated at the densities shown at the top concurrently with S. aureus strain NRS049, inoculated at ∼107 CFU/ml. The agar plates were incubated overnight at 37°C.