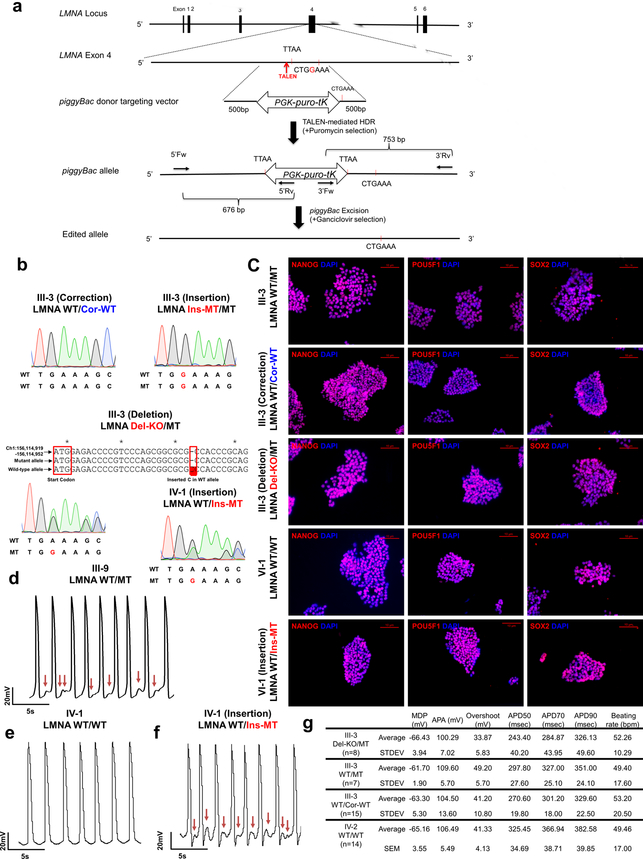
Extended Data Fig. 2. LMNA mutation as a cause of arrhythmic phenotype in LMNA mutant iPSC-CMs.
a, Gene editing strategy using TALEN method. The piggyBac system was utilized to generate isogenic lines as previously described11,12. b, Genotyping of gene-edited isogenic lines (III-3; corrected, insertion, deletion) (IV-1 insertion). For LMNA Del-KO/MT, we utilized TALEN pairs that target the start codon of the LMNA gene. Genotyping showed C insertion in wild-type allele that reads early stop codon. c, Immunostaining of NANOG (Red), POU5F1 (Red), and SOX2 (Red) in iPSC lines. Blue signal represents DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm. The experiments in c were repeated twice independently with similar results. d-f, Electrophysiological recordings of spontaneous action potentials in control (IV-1) and mutant iPSC-CMs (III-9, isogenic IV-1; WT/Ins-MT) measured by patch clamp in current-clamp mode. Red arrows indicate DAD-like arrhythmias. The experiments were repeated three times independently with similar results. g. EP parameters. MDP: maximal diastolic potential; APA: action potential amplitude; APD: action potential duration at 50%, 70%, 90% of repolarization; bpm: beats per minute.