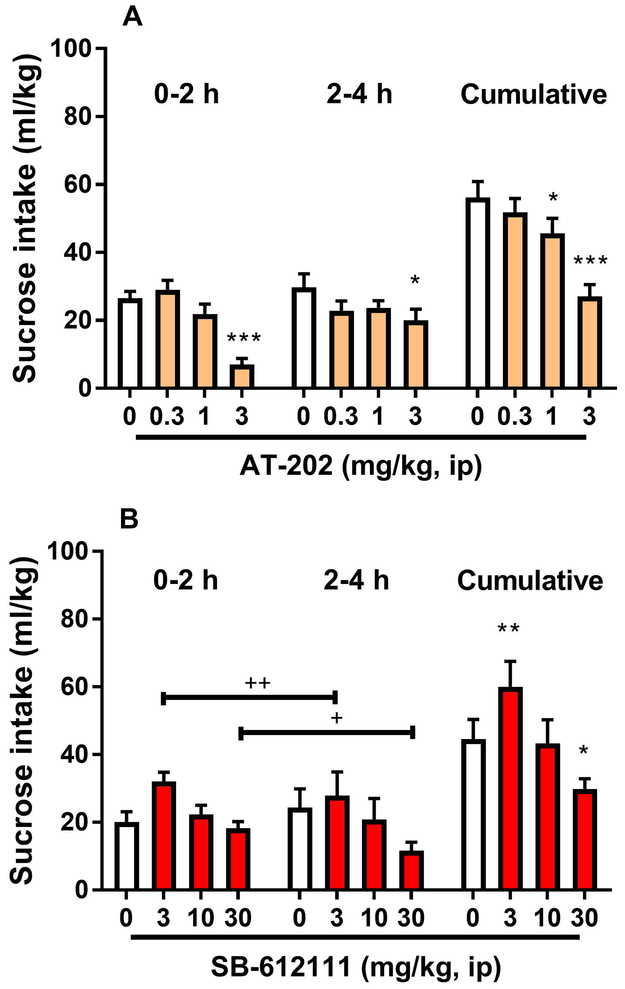
Figure 3.
Effects of administration of the NOP receptor agonist AT-202 and the antagonist SB-612111 on sucrose consumption. Mice received injection (ip) of (A) AT-202 (0, 0.3, 1, 3 mg/kg) or (B) SB-612111 (0, 3, 10, 30 mg/kg) 30 min prior to the start of the 4-h test drinking session of the DID procedure with 0.5% (w/v) sucrose, respectively. AT-202 treatment reduced sucrose consumption. SB-612111 increased sucrose intake at low dose (3 mg/kg) while decreasing consumption at the figh dose examined (30 mg/kg). All data are presented as mean (± SEM) sucrose intake in 2-h fractions (0-2 h & 2-4 h) and as mean (± SEM) cumulative (0-4 h) sucrose intake (ml/kg) of N=9–10 mice per group. * p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 difference from vehicle groups (0 mg/kg). +p<0.05, ++p<0.01 difference from vehicle groups. Connecting line with single or double plus (+ or ++) indicates combined post hoc testing. For detailed statistics, see “Results”.