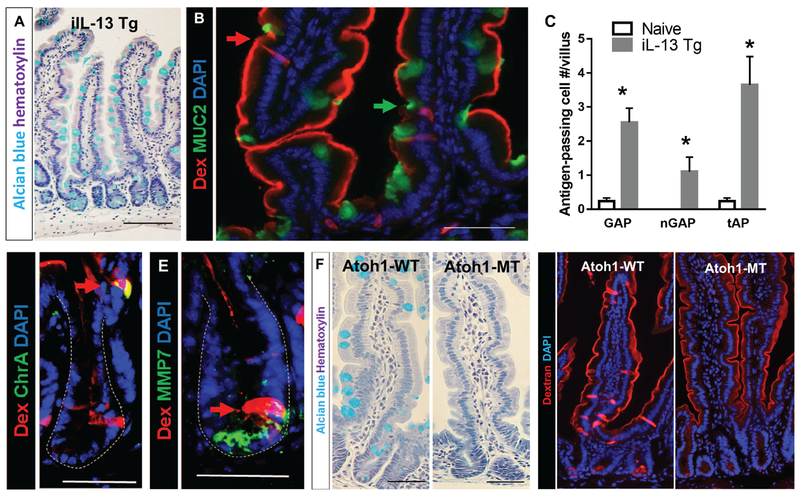
Figure 3. IL-13 is sufficient to drive SAP formation and secretory cells are required for SAP formation.
(A) Alcian blue stain with hematoxylin counterstain on ilL-13 Tg mouse SIs to visualize mucin-producing goblet cells. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis for MUC2 with iIL-13Tg mouse SI. Red arrow points to MUC2− antigen-passages cells, and green arrow points to MUC2+ GAP. (C) Quantification of antigen positive cells in iIL-13 Tg and naïve control mouse SIs; n = 3-4 per group. MUC2− antigen positive cells are denoted as nGAP. Total antigen passages (MUC2+ and MUC2-) are denoted as tAP. (D & E) Immunofluorescence analysis for (D) ChrA, enteroendocrine cell marker or (E) MMP7, Paneth cell marker in iIL-13 Tg mouse SI crypts. Dotted lines indicate basolateral edges of crypts. (F) Alcian blue stain with hematoxylin counterstain on control (Atoh1-WT) and Atohl-deleted (Atoh1-MT) mouse SIs to visualize mucin-producing goblet cells. (G) Immunofluorescence analysis of control (Atoh1-WT) and Atohl-deleted (Atoh1-MT) SIs that were exposed to Rh-Dex. Mice were injected with IL-13 24 h prior to Rh-Dex exposure. Nucleus was visualized with DAPI. Scale bars are 50 μm.