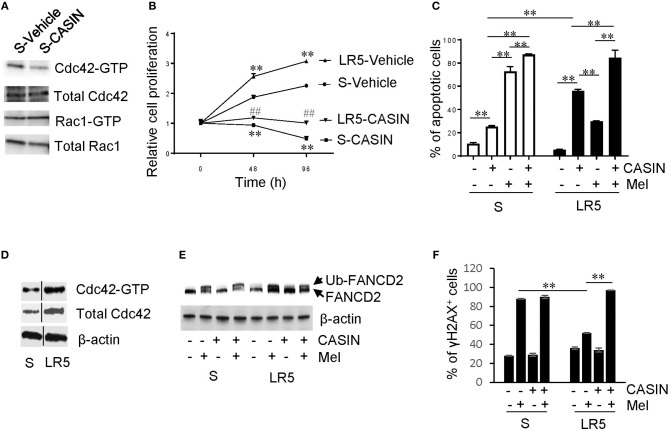
Figure 3.
Effects and mechanism of action of CASIN on melphalan-resistant MM cells. (A) CASIN reduces Cdc42 activity (Cdc42-GTP) but not Rac1 activity (Rac1-GTP). Melphalan-sensitive MM cells (S) were treated with Vehicle or CASIN (5 μM) for 8 h. Cdc42 and Rac1 activities were measured using pull-down assay. (B) CASIN (5 μM) inhibits proliferation of both S and melphalan-resistant (LR5) MM cells. **P < 0.01 vs. S-Vehicle; ##P < 0.01 vs. LR5-Vehicle. (C) CASIN (5 μM) preferentially causes apoptosis of melphalan-resistant MM cells. S and LR5 cells were treated with or without CASIN or melphalan (Mel, 25 μM) or both for 2 days. Annexin V+ cells were analyzed using flow cytometry. **P < 0.01. (D–F) Mechanism of action of CASIN on melphalan-resistant MM cells. (D) Cdc42 activity and expression are increased in LR5 cells compared to that in S cells. Cdc42 activity was measured using pull-down assay. β-Actin was used as loading control. Vertical lines indicate the gel lanes being switched in position from the original blots. (E) CASIN (5 μM) decreases melphalan-induced FANCD2 mono-ubiquitination (Ub-FANCD2) in LR5 but not in S cells. S and LR5 cells were treated with or without CASIN, Mel (25 μM), or both for 16 h. FANCD2 was detected using western blotting. β-Actin was used as loading control. (F) CASIN sensitizes melphalan-resistant but not -sensitive MM cells to melphalan-induced DNA damage. γ H2A histone family member X-positive (γH2AX+) cells were detected using flow cytometry. **P < 0.01. Error bars represent means ± SD of triplicates and data are representative of three independent experiments.