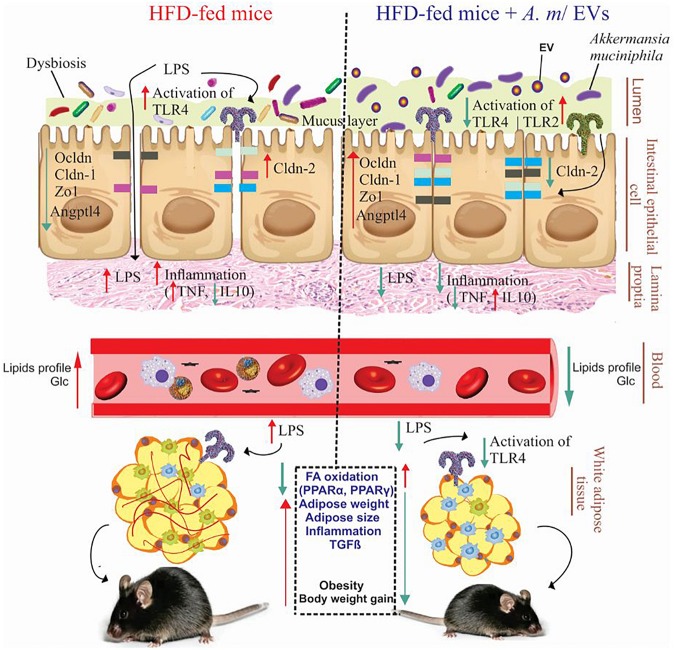
FIGURE 6.
Administration of A. muciniphila and its EVs improves the intestinal and metabolic homeostasis in obese mice. Obesity is associated with the disruption of the intestinal barrier integrity, inflammation, and fat mass gain (left). Oral administration of A. muciniphila or its EVs increase the expression of tight junction proteins and TLR-2 and reduce the expression of TLR-4 and pro-inflammatory cytokines in the colon of obese mice (right). Also, treatment with A. muciniphila and its EVs affects FA oxidation, local inflammation genes, and fat-mass loss in the EAT of obese mice. HFD, high-fat diet; EVs, extracellular vesicles; TLR, toll-like receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; Zo-1, zonula occludens-1; Ocldn, occludin; Cldn, claudin; Angptl4, angiopoietin-like 4; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-10, interleukin-10; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; and Glc, glucose.