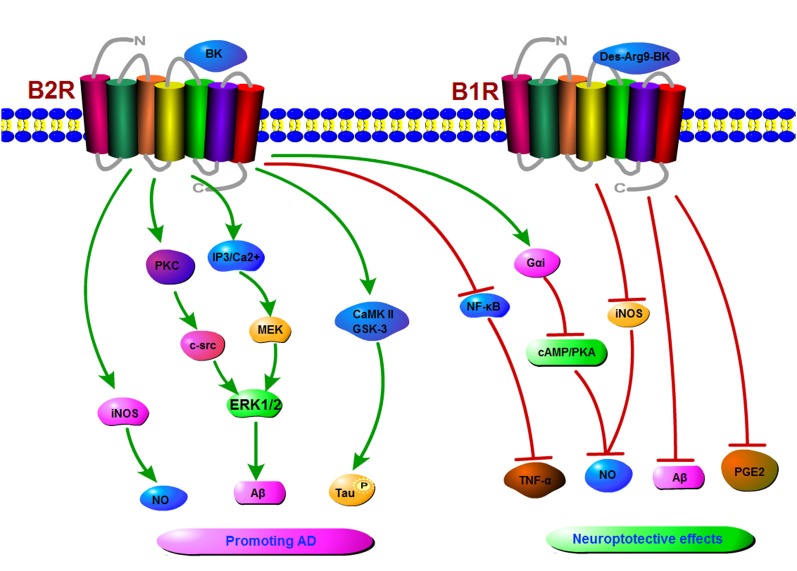
Figure 2.
A schematic diagram of signaling pathways mediated by the KKS in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The binding of kinins to B1R or B2R induces the activation of protein kinase C (PKC), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), extracellular regulated protein kinases1/2 (ERK1/2), CaMKII, ultimately resulting in an increase in NO, tau phosphorylation, and amyloid β (Aβ) production in AD. On the other hand, kinins receptors might play a neuroprotective role in AD by inhibiting the production of NO, Aβ, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) etc.