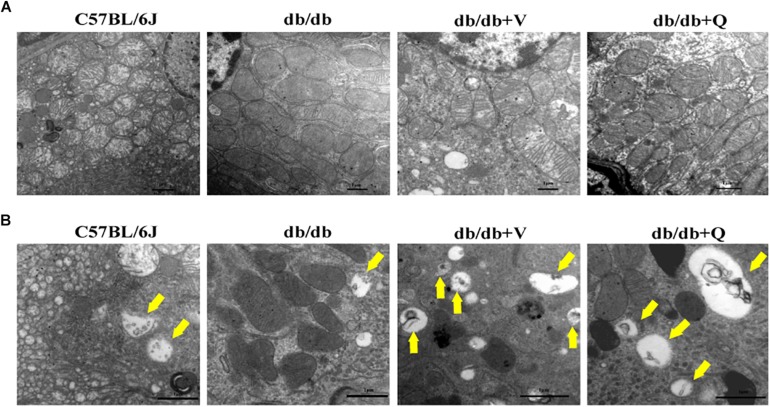
FIGURE 3.
QDTS improved mitochondrial damage and autophagy in renal tubular epithelial cells. (A) Mitochondrial damage. Compared with the normal control group, massive mitochondria with incomplete boundary arranged tightly in the renal tubular epithelial cells of the db/db group, which meant that the damaged mitochondria accumulated and couldn’t be degraded timely; the blurred mitochondrial crista and disappeared double-layer membrane constructor implied that the ability of oxidative phosphorylation decreased (×40000). Valsartan and QDTS alleviated these damages of mitochondria to some extent. (B) Autophagic vacuoles. Compared with the normal control group, the number of autophagic vacuoles in the tubular epithelial cells of db/db mice was decreased, and the volume was relatively smaller (×70000). The number and volume of autophagic vacuoles in the valsartan and QDTS groups were significantly improved.