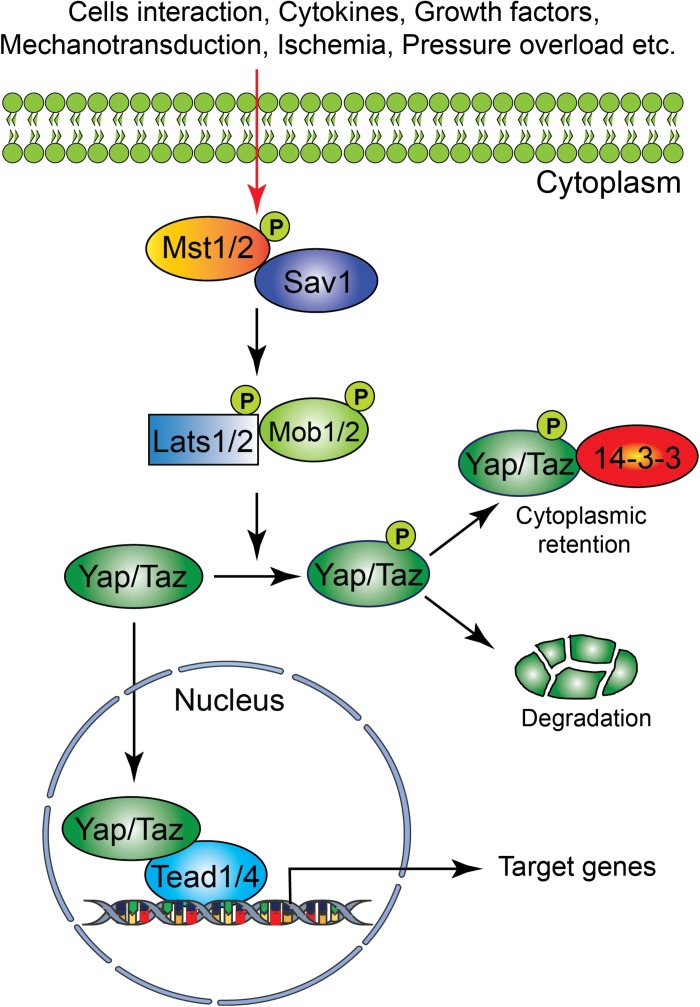
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of the core components of the Hippo signaling pathway. Several physiological and pathological signals can activate the Hippo signaling pathway in the heart. The physiological signal includes cell–cell interaction, cytokines, and growth factors, whereas the pathological signal includes oxidative stress (ischemia-reperfusion injury), mechanical stress (pressure overload) and injury (myocardial infarction). The core Hippo signaling pathway consists of serine/threonine kinases, transcriptional coactivators, and transcription factors. Upon activation, the upstream kinases (Mst1/2, Lats1/2, Sav1, and MOB1) promote phosphorylation of downstream mediators Yap and Taz, resulting in their cytoplasmic retention or degradation. In contrast, inactivation of upstream kinases leads to nuclear translocation of Yap and Taz, where they bind to various transcription factors including Tead factors (Tead1-4) and regulate target gene expression.