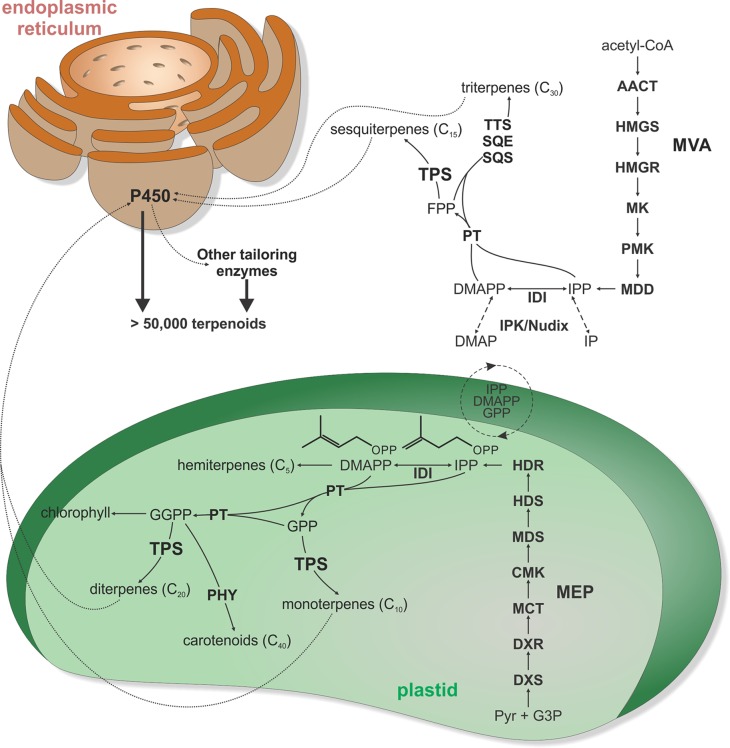
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of major terpenoid biosynthetic pathways. All terpenoids are derived from two isomeric 5-carbon precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP), and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). In turn, IPP and DMAPP are formed via two pathways, the cytosolic mevalonate (MVA) pathway originating from acetyl-CoA and the pyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)–derived 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway located in the plastids. However, active transfers of IPP, DMAPP, GPP, and FPP across the plastidial membrane enable some degree of pathway cross-talk. In addition, interconversion of IPP and DMAPP with their respective monophosphate forms IP and DMAP by IP kinase (IPK) and Nudix hydrolase enzymes can impact pathway flux in terpenoid metabolism. Except for isoprene and hemiterpene (C5) biosynthesis, condensation of IPP and DMAPP units generates prenyl diphosphate intermediates of different chain length. Condensation of IPP and DMAPP yields geranyl diphosphate (GPP) as the precursor to monoterpenoids (C10), fusing GPP with an additional IPP affords the sesquiterpenoid (C15) precursor farnesyl diphosphate (FPP), and fusing FPP with IPP generates geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) en route to diterpenoids (C20). Furthermore, condensation of two FPP or two GGPP molecules forms the central substrates of triterpenoid (C30) and carotenoids (C40), respectively. Terpene synthases (TPS) are key gatekeepers in the biosynthesis of C10–C20 terpenoids, catalyzing the committed scaffold-forming conversion of the respective prenyl diphosphate substrates into a range of hydrocarbon or oxygenated structures. These TPS products can then undergo various oxygenations through the activity of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (P450), followed by further possible functional decorations, ultimately giving rise to more than 80,000 distinct natural products. AACT, acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase; CMK, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase; DXR, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductase; DXS, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase; HDR, (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl diphosphate reductase; HDS, (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl diphosphate synthase; HMGR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; HMGS, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase; IDI, isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase; MCT, MEP cytidyltransferase; MDD, mevalonate-5-diphosphate decarboxylase; MDS, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; MK, mevalonate kinase; P450, cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase; PHY, phytoene synthase; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase; PT, prenyl transferase; SCS, squalene synthase; SQE, squalene epoxidase; TPS, terpene synthase; TTS, triterpene synthase.