Figure 4.
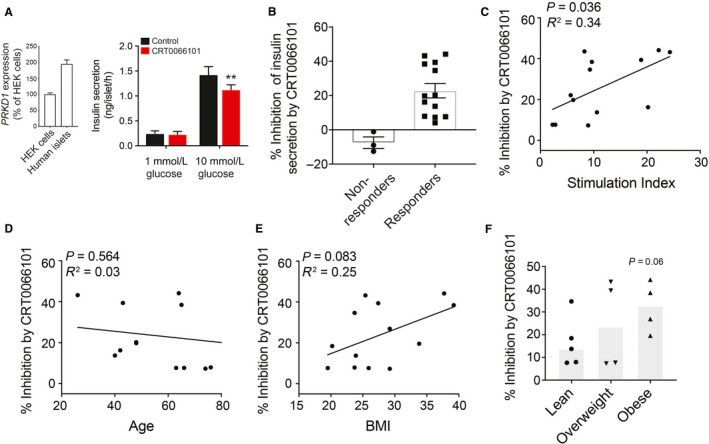
Ability of PKD1 to potentiate insulin secretion positively correlates with stimulation index and BMI of humans. (A) At right, we confirm the expression of transcript encoding PKD1 (PKRD1) in human islets, and at left we measure insulin secretion in (ng/islet/hr) in 1‐h static incubations in response to 1 and 10 mmol/L glucose in the presence of PKD1 inhibitor, CRT0066101 (10 μmol/L). (B) Comparison of donor–donor response according to percentage inhibition of insulin secretion by PKD1 antagonist. (C–E) The percentage inhibition of responders after 20 min CRT0066101 treatment plotted against stimulation index (panel C; n = 13 donors), age (panel D; n = 13 donors), and BMI (kg/m2; panel E; n = 13 donors) in nondiabetic human islet donors. (F) Comparison of percentage inhibition by MRS2500 according to BMI tertiles (lean < 25; overweight 25–30; and obese> 35 kg/m2) (n = 5, 4, 4 donors).
