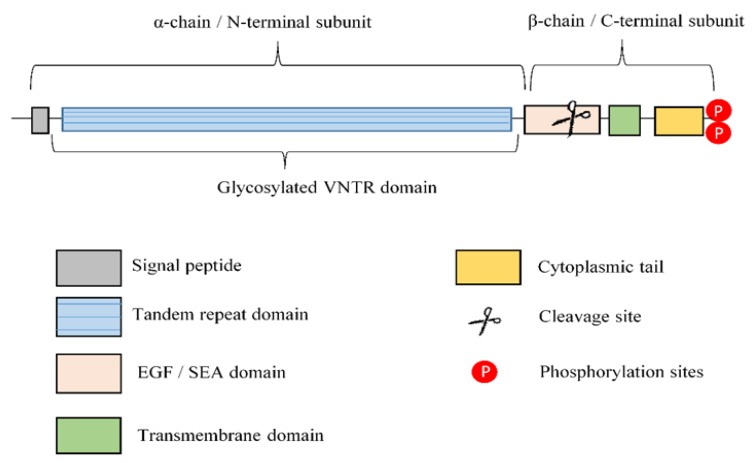
Figure 2.
General structure of the transmembrane mucins. Transmembrane mucins are composed of two subunits: α chain or N-terminal subunit and β chain or C-terminal subunit, based on the putative proteolytic cleavage site in the epidermal growth factor/sperm protein, enterokinase and agrin (EGF/SEA) domain. The α-chain is extracellular and predominantly composed of variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) highly glycosylated. The β-chain consists of a short extracellular region (containing either SEA domain or EGF-like domain), single transmembrane (TM) domain, and the cytoplasmic tail, which contains multiple phosphorylation sites.