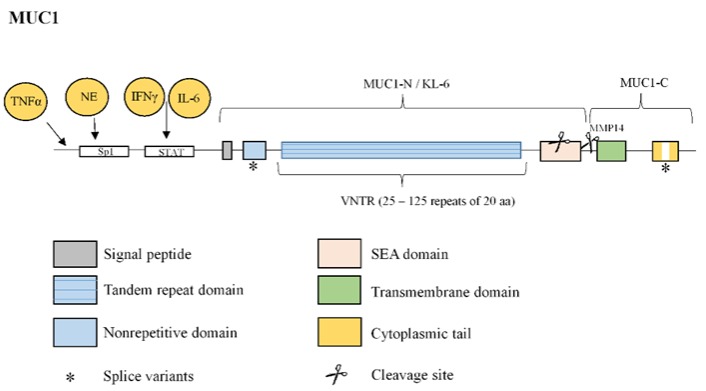
Figure 6.
Structure of mucin MUC1. MUC1 protein is comprised of an N-terminal subunit (also called KL-6) constituted by an extracellular variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) domain composed of 25–125 repeats of 20 amino acids, and a C-terminal subunit constituted by a SEA domain, a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic tail (CT). MUC1 extracellular domain can be shed into the lumen by proteolytic cleavage in the SEA domain or by the action of metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14) in the region following the SEA domain. Two examples of splice variants of MUC1 transcript are shown (*): a nonrepetitive sequence insertion prior to the variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) region and variations in the CT. MUC1 overexpression is induced by activation of the single STAT-binding site of MUC1 promoter by interferon (IFN)γ or interleukin (IL)-6 or by an increased Sp1 binding to MUC1 promoter by neutrophil elastase (NE). Tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) also upregulates the transcription of MUC1.