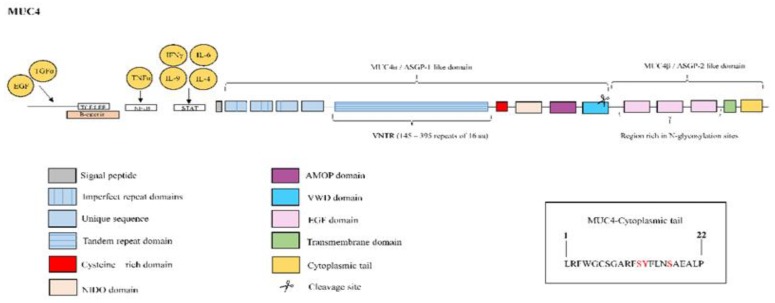
Figure 9.
Structure of mucin MUC4. MUC4 protein is constituted by the ASGP-1-like extracellular domain or MUC4α, which contains an N-terminal signal sequence followed by: three imperfect repeats, an unique sequence, a variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) composed of 145–395 repeats of 16 amino acids, a cysteine-rich domain, nidogen-like domain (NIDO), adhesion-associated domain in MUC4 and other proteins (AMOP) and Von Willebrand factor type D domain (vWD). The cleavage site is located in this vWD domain. The ASGP-2-like or MUC4β subunit is rich in N-glycosylation sites and contains up to three EGF-like domains, a hydrophobic transmembrane region, and a 22-amino-acid cytoplasmic tail. The right box contains the amino acid sequence of the cytoplasmic tail with potential sites for phosphorylation marked in red color. MUC4 overexpression is induced by interleukin (IL)-9, IL-4 and IL-6 mediated JAK/STAT pathway activation. Combined treatment with tumour necrosis factor (TNF)α and interferon (IFN)-γ has been also shown to upregulate MUC4 expression through nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and JAK/STAT pathways respectively. The growth factors epidermal growth factor (EGF) and transforming growth factor α (TGα) also upregulate MUC4 expression. Three T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF)-binding sites on the MUC4 promoter and the binding of β-catenin has been demonstrated on MUC4 promoter.