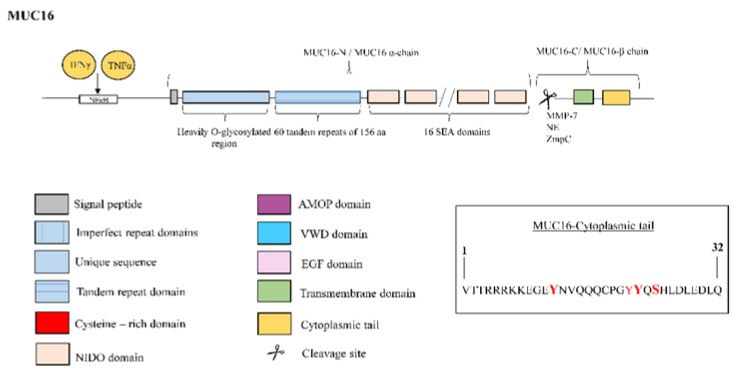
Figure 11.
Structure of mucin MUC16. MUC16 protein is comprised by two subunits, the MUC16-N terminal or α subunit and the MUC16-C terminal or β subunit. The N-terminal subunit is constituted by a typical, heavily O-glycosylated mucin domain, 60 tandem repeats of 156 amino acids and 16 SEA modules. Otherwise, the C-terminal portion consists of a transmembrane (TM) region and a 32-residue cytoplasmic tail. The right box contains the amino acid sequence of the cytoplasmic tail with potential sites for phosphorylation marked in red color. For the amino acids in bold red font, phosphorylation was demonstrated. MUC16 clevage occurs in the 12 extracellular amino acids domain proximal to the TM domain. Proteases such as metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7), neutrophil elastase (NE) and bacterial metalloprotease (ZmpC) have been implicated in enhanced shedding of MUC16 from the cell surface. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interferon (IFN)-γ stimulate the expression of MUC16 through an nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) response element in the MUC16 promoter.