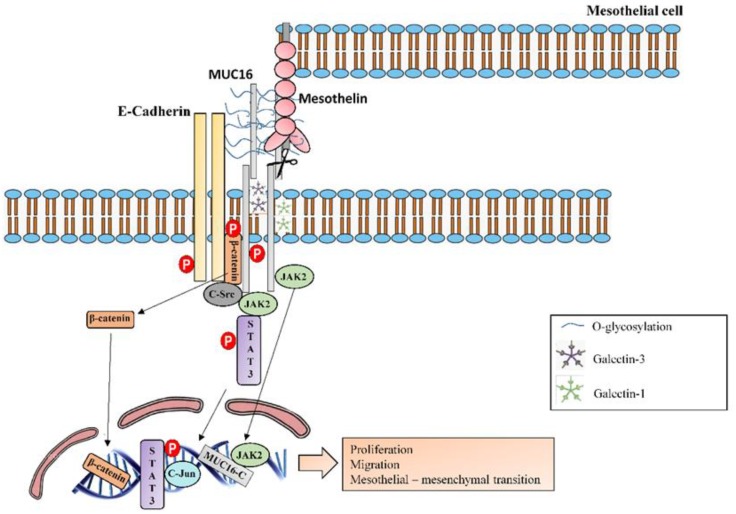
Figure 12.
MUC16 molecular interactions and intracellular signalling. MUC16-C terminal subunit colocalizes into the nucleus with JAK2 and they both impart tumorigenic and metastatic functions. Furthermore, MUC16-C terminal subunit also associates with JAK2 in the cytoplasm and consequently activates STAT3 and c-Jun to promote cell proliferation. MUC16 has been observed associated with E-cadherin and β-catenin complexes and it inhibits GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation and degradation of β-catenin, leading to increased levels of the fibrogenic transcription factor β-catenin. It is suggested that the cytoplasmic tail of MUC16 could bind to β-catenin and that the extracellular domain of MUC16 could interacts with the extracellular domain of E-cadherin and stabilizes E-cadherin at the cell membrane. MUC16-CT directly binds the c-src kinase, which phosphorylate it. C-src also mediates tyrosine phosphorylation of E-cadherin, inducing its ubiquitination and degradation. Otherwise, β-catenin phosphorylation by c-Src negatively regulates the binding to E-cadherin. Therefore, β-catenin is translocated into the nucleus. MUC16 extends from the surface and binds to mesothelin, a protein that is found on the surface of the mesothelial cells, activating MUC16 and enhancing epithelial mesothelial to mesenchymal transition. MUC16 has also been shown to bind with galectin-1 and galectin-3.