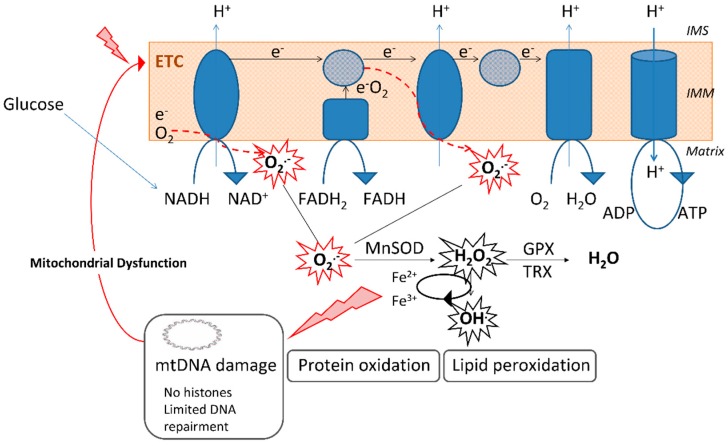
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial superoxide (O2•−) generation by the electron transport chain (ETC) and the implication of the enzyme manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), the only superoxide dismutase enzyme located in the mitochondrial matrix, in its detoxification. The elevated levels of O2•− induce damage to macromolecules, including lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, and promote mitochondrial dysfunction. Absence of histones in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and limited DNA repair mechanisms make mitochondria highly susceptible to DNA damage induced by O2•−. ADP: Adenoxine diphosphate; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; GPX: Glutathione peroxidase; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; IMM: Inner mitochondrial membrane; IMS: Intermembrane space; O2•−: Superoxide anion; OH•: Hydroxyl radical; TRX: Thioredoxin reductase.