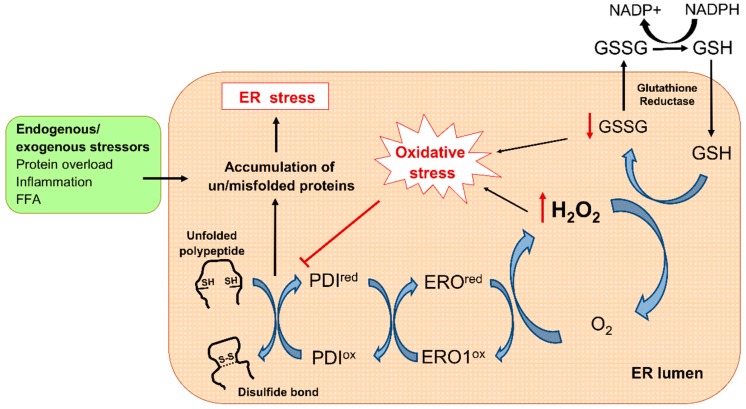
Figure 2.
Oxidative protein machinery and ER stress. During disulfide bond formation, two electrons are transferred to the pair of cysteines in the polypeptide by the PDI active site. Thereafter, reduced PDI receive electrons from O2 through ERO1-mediated redox reaction, resulting in H2O2 formation. The GSH/GSSG system then recovers the redox status by scavenging H2O2. Several stimuli including increased protein synthesis demand overwhelm ER-folding capacity and disturb redox balance, leading to the accumulation of misfolded proteins and triggering ER stress. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; ERO1: ER oxidoreductin 1; FFA: Free fatty acids; GSH: Glutathione; GSSG: Glutathione disulphide; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; PDI: Protein disulfide isomerase.