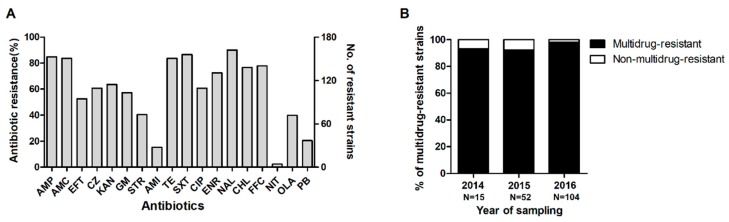
Figure 4.
Resistance of the E. coli isolates from piglets with diarrhea to various antimicrobial agents. (A) The frequency of antibiotic resistance and the number of resistant strains among intestinal pathogenic E. coli from Chinese large-scale swine farms. (B) Proportion of multidrug-resistant strains between 2014 and 2016. The results of the tests for ampicillin (AMP), amoxicillin–clavulanate (AMC), ceftiofur (EFT), cefazolin (CZ), kanamycin (KAN), gentamicin (GM), streptomycin (STR), amikacin (AMI), tetracycline (TE), trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole (SXT), ciprofloxacin (CIP), enrofloxacin (ENR), nalidixic acid (NAL), chloramphenicol (CHL), florfenicol (FFC), nitrofurantoin (NIT), olaquindox (OLA), and polymyxin B (PB) were interpreted according to CLSIM100-S26 and CLSI VET01-A4 guidelines. Multidrug-resistant isolates were those resistant to three or more antimicrobial classes, and intermediate isolates were not included.