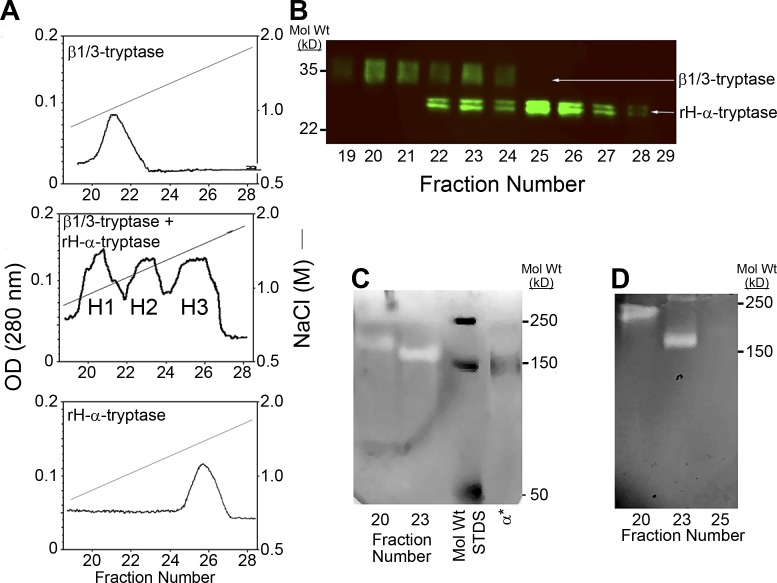
Figure 1.
Formation of α/β-tryptase heterotetramers in vitro. (A) Heparin-Sepharose chromatography of homotypic and heterotypic tetramers of natural HMC1-derived β1/3-tryptases and rH-α1-tryptase. Protryptases β1/3 (top), α (bottom), and β1/3 + α (middle) were activated with human CTSB and separated by heparin-Sepharose chromatography with a linear NaCl gradient into three overlapping protein peaks, labeled H1, H2, and H3. Only H1 and H2 were catalytically active. (B) Peak heparin-Sepharose fractions were reduced, denatured, and analyzed by Western blotting with the G3 anti-tryptase mAb. (C) Peak heparin-Sepharose fractions, nonreduced and nondenatured, were analyzed by gelatin zymography along with labeled mol wt standards (STDS) and IRDye 800–labeled α1-tryptase homotetramers (α*). (D) Gelatin zymography after extended electrophoresis to better separate putative α/β-tryptase heterotetramers from β-tryptase homotetramers. Representative of two independent experiments.