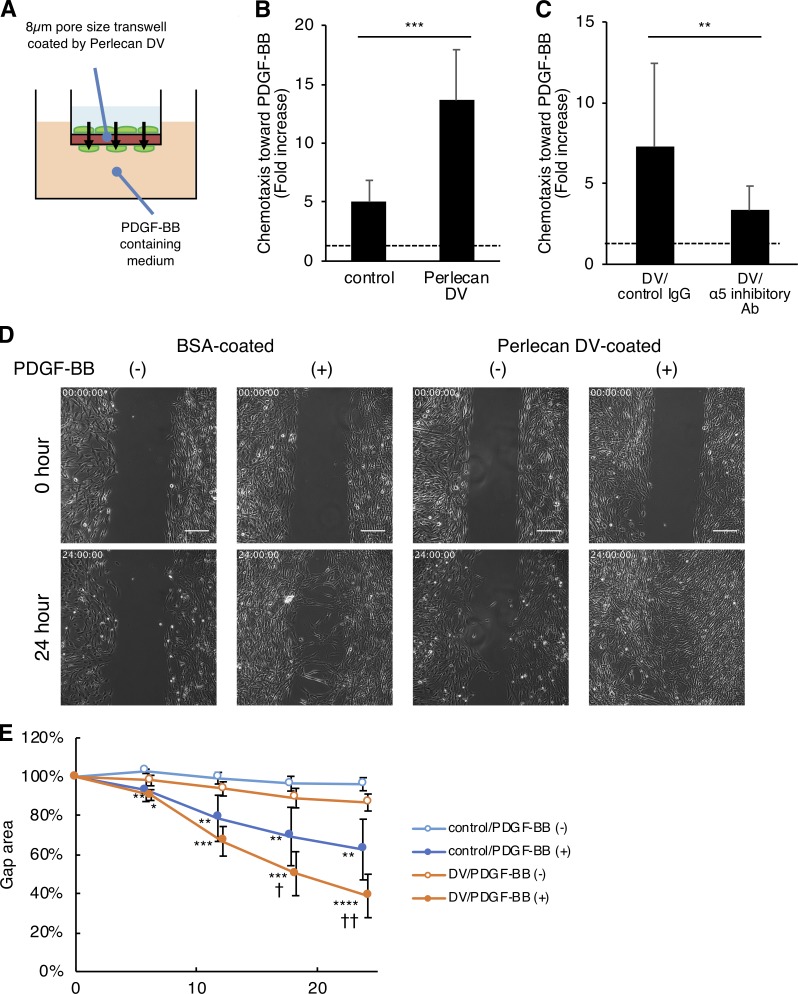
Figure 6.
Perlecan DV promotes the PDGF-BB–induced migration of pericytes. (A and B) Brain pericytes migrating toward PDGF-BB (50 ng/ml) through a membrane coated with BSA (control) or perlecan DV (500 nmol/liter), normalized against a no-chemoattractant negative control. Values are mean ± SD from three independent experiments conducted in triplicate; ***, P < 0.001, unpaired t test. (C) The migration of brain pericytes treated with control IgG or integrin α5 inhibitory Ab (mAb16) toward PDGF-BB (25 ng/ml) through a membrane coated with perlecan DV (500 nmol/liter), normalized against a no-chemoattractant negative control. Values are mean ± SD from four independent experiments with triplicates; **, P < 0.01, unpaired t test. (D) Brain pericytes cultured with a 500-µm-wide gap insert on plates coated with BSA (control) or perlecan DV (500 nmol/liter) were treated with or without PDGF-BB (50 ng/ml) in serum-free medium. Representative images for the wound healing at 0 and 24 h are shown. Scale bar = 250 µm. (E) The cell-covered area of the wound healing assay was analyzed with ImageJ and is shown as a percentage of the initial gap area. Values are mean ± SD; n = 4–6 per group; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001 versus without PDGF-BB; †, P < 0.05; ††, P < 0.01 versus control substrate (BSA), one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer’s HSD test.