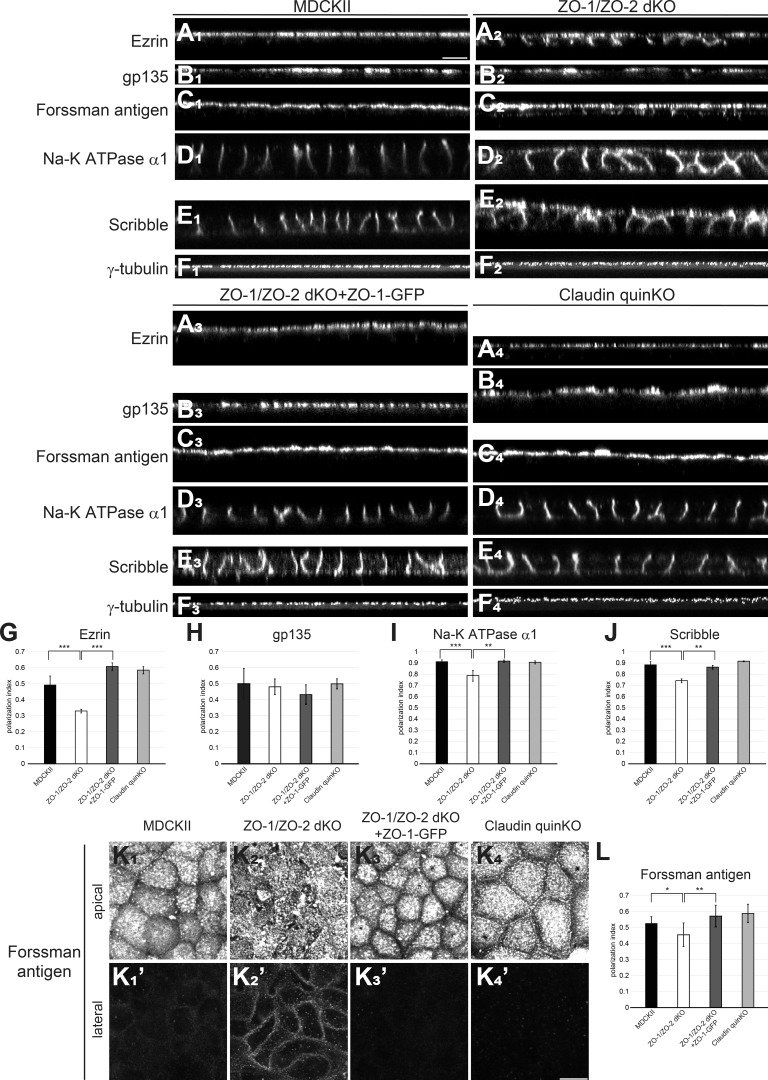
Figure 5.
ZO-1/ZO-2 regulates epithelial polarity. (A–D) Immunofluorescence analyses of polarity markers. (A1–F1) In MDCK II cells, ezrin (A1), gp135 (B1), and Forssman antigen (C1) were selectively localized to the apical membrane, while Na-K ATPase α1 subunit (D1) and Scribble (E1) were restricted to the basolateral membrane. γ-Tubulin staining (F1) shows that centrosomes are aligned in the apical cytoplasm. (A2–F2) In ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells, epithelial polarity was disorganized, and ezrin (A2), Forssman antigen (C2), Na-K ATPase α1 subunit (D2), and Scribble (E2) were detected on both the apical and basolateral membranes, while gp135 (B2) or γ-tubulin (F2) localization was not severely perturbed. (A3–F3) Expression of ZO-1–GFP rescued the epithelial polarity phenotypes of ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells. (A4–F4) No epithelial polarity defects were observed in claudin quinKO cells. (G–J) Quantitation of polarization index of ezrin (G), gp135 (H), Na-K ATPase α1 subunit (I), and Scribble (J). Graphs represent mean ± SD (n = 3–9). (K) Forssman antigen localization in apical (K1–K4) and lateral (K′1–K′4) confocal sections. (L) Quantitation of polarization index of Forssman antigen. Graphs represent mean ± SD (n = 6–15). All cells were cultured on Transwell filters for 5–7 d. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005, compared by t test. Scale bars: 10 µm.