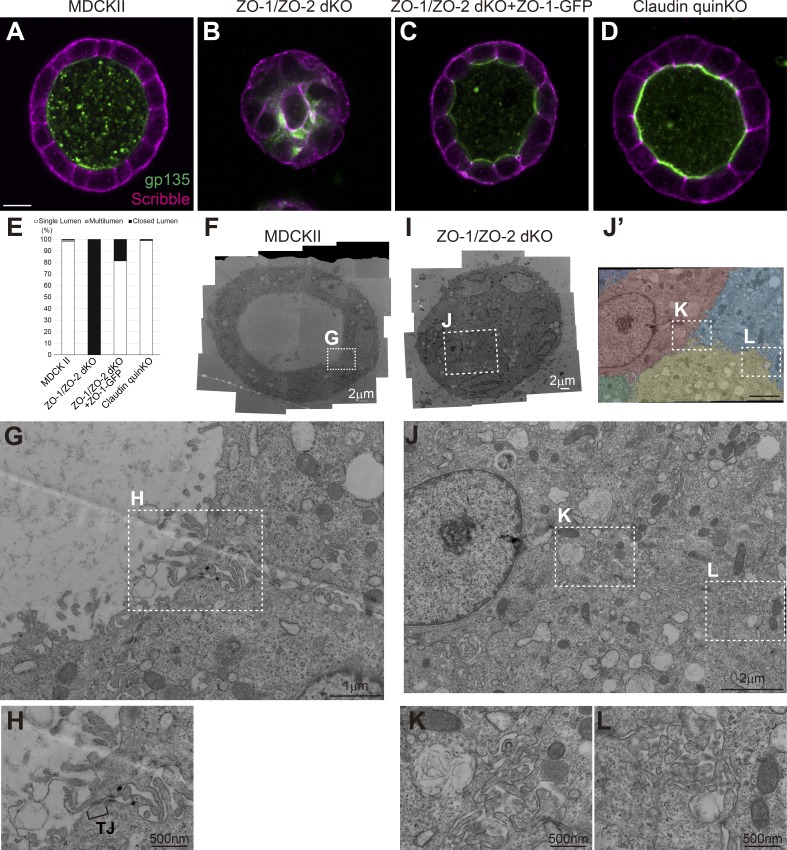
Figure 6.
ZO-1/ZO-2 regulates polarized cyst formation. (A–D) Localization of apical marker gp135 (green) and basolateral marker Scribble (magenta) in cells embedded in collagen I gels and cultured for 5–7 d. (A) MDCK II cells formed polarized cysts. (B) ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells failed to expand their lumens and did not form polarized cysts. Occasional colocalization of gp135 and Scribble was observed. (C) ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells were able to form polarized cysts upon expression of ZO-1–GFP. (D) Claudin quinKO cells formed polarized cysts. (E) Quantitation of cyst phenotypes (n = 343 for MDCK II, n = 536 for ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO, n = 311 for ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO + ZO-1–GFP, n = 752 for claudin quinKO). (F–H) Transmission EM observation of cysts formed by MDCK II cells. MDCK II cells formed a polarized epithelium in the collagen gels, and TJs were formed at the most apical region of the intercellular junctions (H). (I–L) Transmission EM observation of ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells embedded in collagen I gels. The lumens failed to expand in ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells, and microvilli and microlumens were observed between the cells (K and L). The cells were pseudocolored in J′. White squares indicate the regions shown in high-magnification images. Scale bars: 10 µm (A–D); 2 µm (F and I); 1 µm (G and J); 500 nm (H, K, and L).