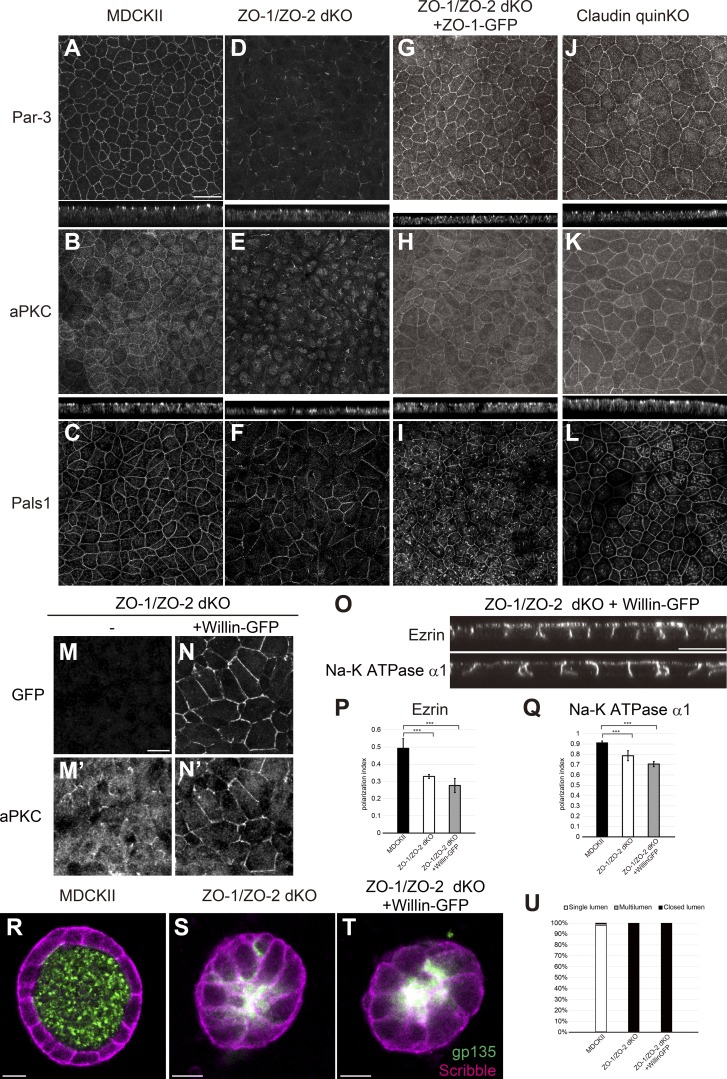
Figure 9.
Polarity signaling molecules are mislocalized in ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells. (A–C) Par-3 (A), aPKC (B), and Pals1 (C) were localized to apical junctions in MDCK II cells. (D–F) Par-3 (D) and aPKC (E) were diffuse and fragmented in ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells. Pals1 (F) localization was fragmented to a smaller extent in ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells. (G–I) Apical junction localization of Par-3 (G), aPKC (H), and Pals1 (I) was restored by expression of ZO-1–GFP in ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells. (J–L) Par-3 (J), aPKC (K), and Pals1 (L) were able to localize to apical junctions in claudin quinKO cells. Apical confocal sections are shown for Pals1, and the intracellular signals are nonspecific staining. (M and N) Willin-GFP overexpression promoted apical junction localization of aPKC in ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells. (M) aPKC localization was diffuse and fragmented in ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells. (N) Willin-GFP overexpression promoted apical junction localization of aPKC. GFP (M and N); aPKC (M′ and N′). (O) Willin-GFP overexpression did not restore the polarized localization of ezrin and Na-K ATPase α1 subunit in ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells. (P and Q) Quantitation of polarization index of ezrin (P) and Na-K ATPase α1 subunit (Q). Graphs represent mean ± SD (n = 10 each). ***, P < 0.0005, compared by t test. (R–T) Localization of apical marker gp135 (green) and basolateral marker Scribble (magenta) in MDCK II cells (R), ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO cells (S), and ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO + Willin-GFP cells (T) embedded in collagen I gels and cultured for 5–7 d. Willin-GFP expression did not rescue the lumen phenotype. (U) Quantitation of cyst phenotypes (n = 368 for MDCK II, n = 536 for ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO, n = 1,061 for ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO + Willin-GFP). Data for ZO-1/ZO-2 dKO are identical to Fig. 7 E. Scale bars: 20 µm (A–L and O); 10 µm (M, N, and R–T).