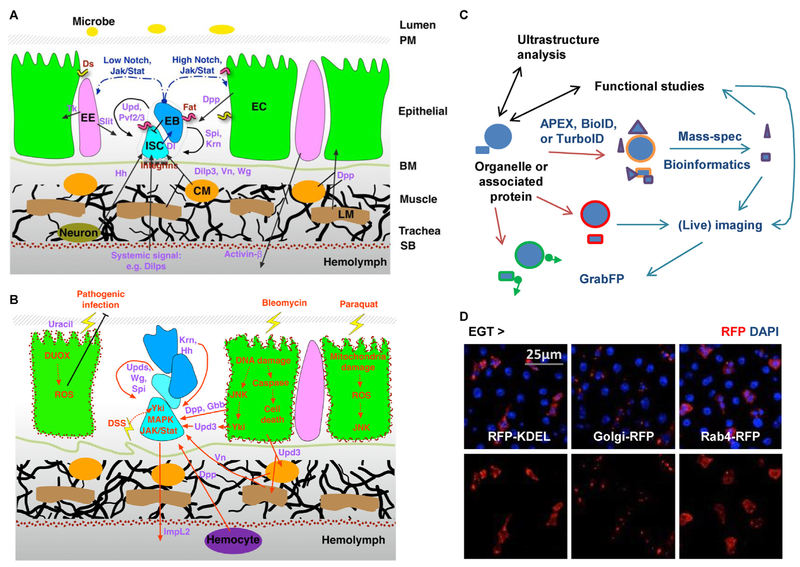
Figure 3.
Future perspectives of organelle studies in the midgut. (A) The organization of different cell types and the cell communication network in the midgut under homeostatic conditions. Ligands for different signaling pathways are highlighted in purple. CM: circular visceral muscle; LM: longitudinal visceral muscle; PM: peritrophic membrane; SB: serosal barrier. (B) Activation of multiple signals in the midgut under stressed conditions. Red arrows indicate signals that are positively affected by tissue damage. DUOX: dual oxidase; DSS: dextran sulfate sodium. (C) Development of new tools will establish a versatile interdisciplinary platform and transform future studies of organelle biology in the midgut. (D) Examples of cell type specific organelle labeling. Midguts expressing RFP-labeled ER (-KDEL), Golgi body, or endosome (Rab4) in ISCs for 4d were co-stained with DAPI.