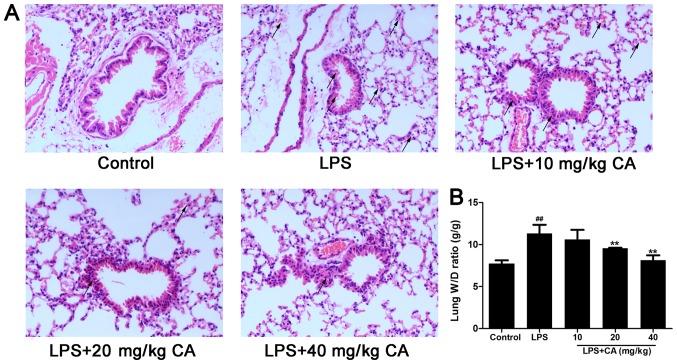
Figure 1.
Injury of lung tissue following exposure to LPS and CA pre treatment. Mice were treated with CA (0, 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg), followed by exposure to LPS (4 mg/kg) or the vehicle control (PBS) 12 h later. At 6 h post LPS/control treatment, the mice were sacrificed for histopathological analysis and edema evaluation. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of lung tissue. No abnormal findings were noted in the control group. Hemorrhage and inflammatory cell infiltration were observed in the LPS-treated groups, but were attenuated by CA (magnification, ×400; indicated with black arrows). (B) W/D ratio of lungs following LPS and CA treatment. ##P<0.01 vs. the control group; **P<0.01 vs. the LPS-treated group. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; CA, carnosicacid; W/D, wet to dry.