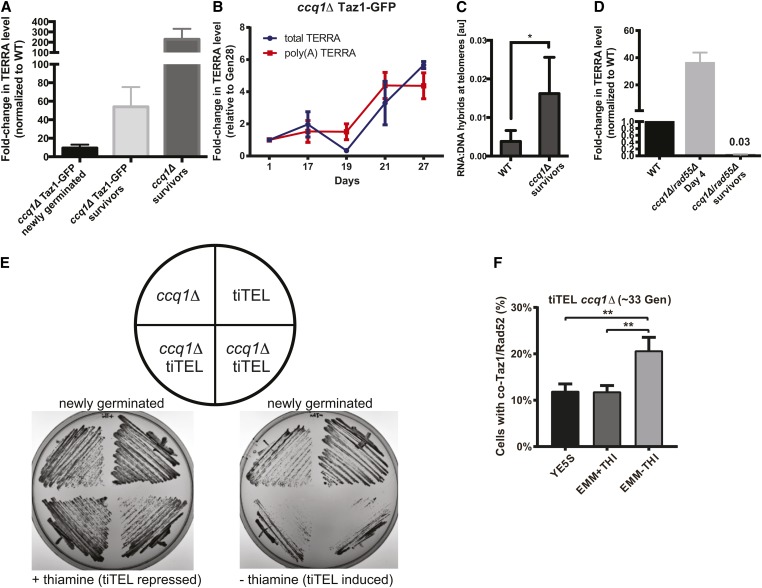
Figure 2.
TERRA is upregulated during ccq1Δ survivor formation but a tiTEL cannot prevent a growth crisis. (A) TERRA levels are higher in ccq1Δ cells shortly after germination, and are dramatically increased in survivors. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for G-rich TERRA normalized to WT cells and plotted as the mean with SD from three replicates. (B) TERRA levels increase concomitant with the emergence of ccq1Δ survivors between days 19 and 27. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for both total and poly(A+) TERRA normalized to Day1 ccq1Δ cells and plotted as the mean with SD from three replicates. (C) Telomeric RNA/DNA hybrids increase in ccq1Δ survivor cells as assessed by DNA-IP using the S9.6 antibody (see Materials and Methods). Mean of three replicates plotted with the SD. * P < 0.05. (D) Newly germinated ccq1Δrad55Δ cells contain high levels of total TERRA shortly after germination but TERRA is depleted in ccq1Δrad55Δ survivors as determined by RT-PCR as in (A). (E and F) tiTEL induction leads to a more rapid and pronounced growth crisis in newly germinated ccq1Δ cells. (E) Culturing of two ccq1Δ tiTEL clones on either EMM + thiamine (tiTEL repressed) or – thiamine (tiTEL induced) solid media. tiTEL induction leads to poorer growth than seen for ccq1Δ cells alone. (F) Increased loading of recombination factors on telomeres in newly germinated ccq1Δ tiTEL cells upon induction. Fluorescence micrographs of newly germinated (33 generations) ccq1Δ tiTEL cells expressing Taz1-GFP and Rad52-mCherry were quantified for colocalization. ** P < 0.01 by Student’s t-test.